Data augmentation to improve robustness of image captioning solutions
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2021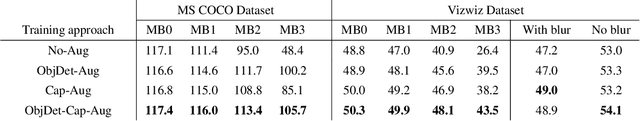
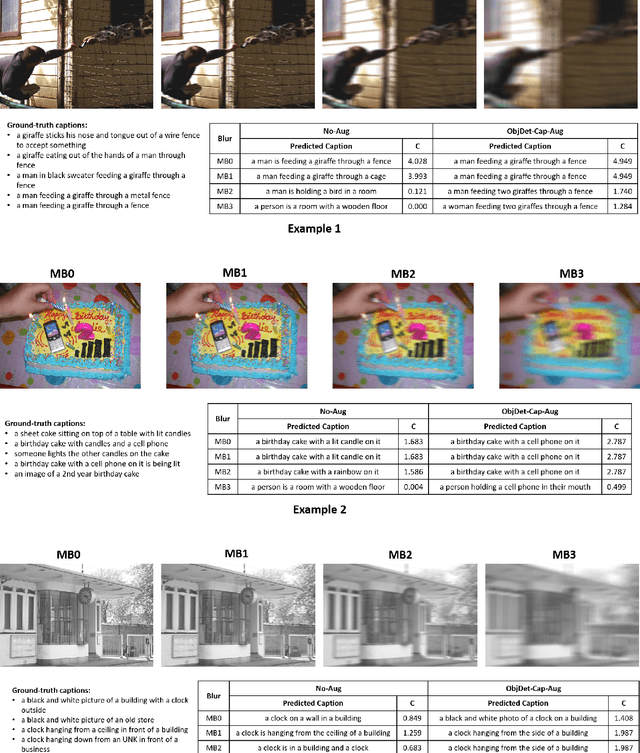
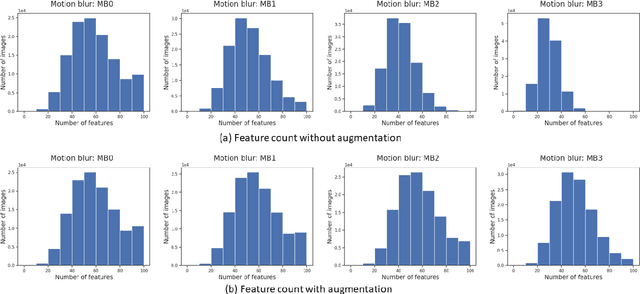
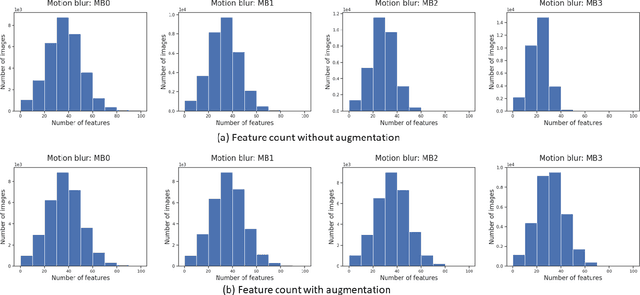
In this paper, we study the impact of motion blur, a common quality flaw in real world images, on a state-of-the-art two-stage image captioning solution, and notice a degradation in solution performance as blur intensity increases. We investigate techniques to improve the robustness of the solution to motion blur using training data augmentation at each or both stages of the solution, i.e., object detection and captioning, and observe improved results. In particular, augmenting both the stages reduces the CIDEr-D degradation for high motion blur intensity from 68.7 to 11.7 on MS COCO dataset, and from 22.4 to 6.8 on Vizwiz dataset.
* CVPR VizWiz 2021 workshop
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge