DA-LMR: A Robust Lane Markings Representation for Data Association Methods
Paper and Code
Nov 17, 2021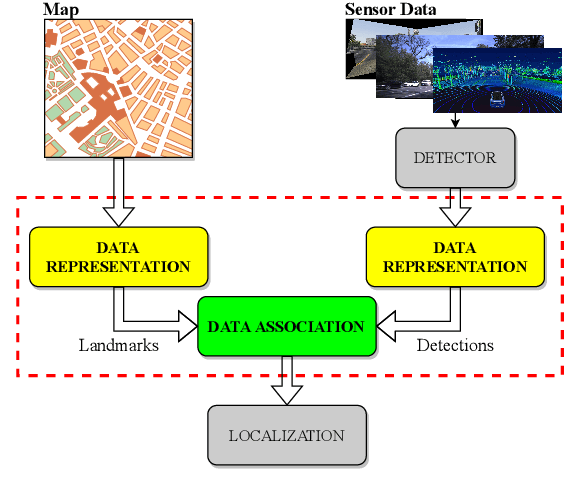
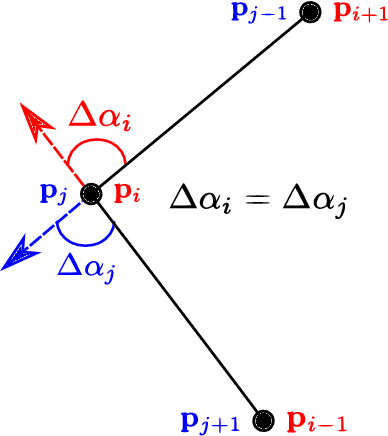
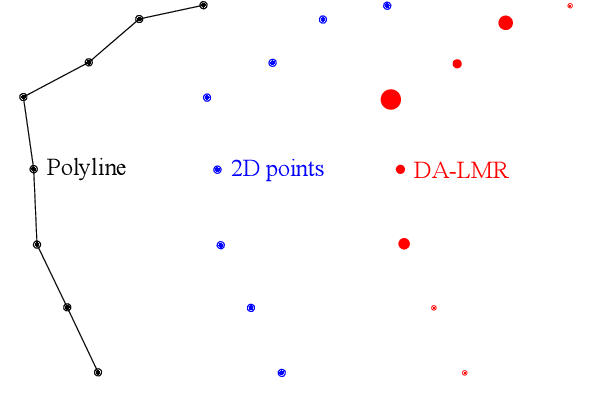
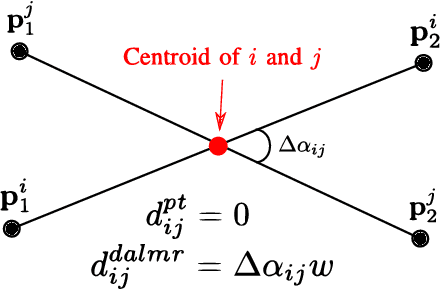
While complete localization approaches are widely studied in the literature, their data association and data representation subprocesses usually go unnoticed. However, both are a key part of the final pose estimation. In this work, we present DA-LMR (Delta-Angle Lane Markings Representation), a robust data representation in the context of localization approaches. We propose a representation of lane markings that encodes how a curve changes in each point and includes this information in an additional dimension, thus providing a more detailed geometric structure description of the data. We also propose DC-SAC (Distance-Compatible Sample Consensus), a data association method. This is a heuristic version of RANSAC that dramatically reduces the hypothesis space by distance compatibility restrictions. We compare the presented methods with some state-of-the-art data representation and data association approaches in different noisy scenarios. The DA-LMR and DC-SAC produce the most promising combination among those compared, reaching 98.1% in precision and 99.7% in recall for noisy data with 0.5m of standard deviation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge