CURTAINs Flows For Flows: Constructing Unobserved Regions with Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Paper and Code
May 08, 2023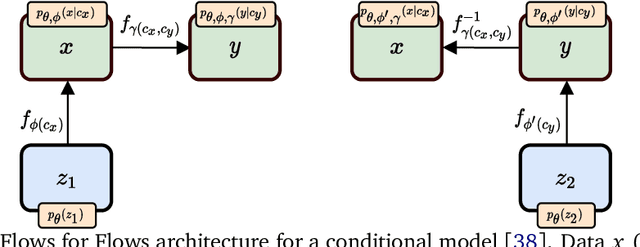
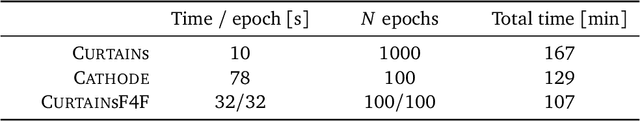
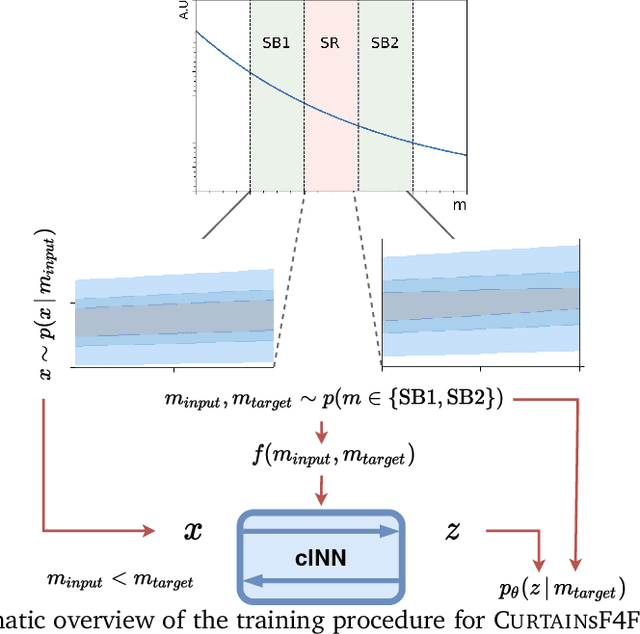
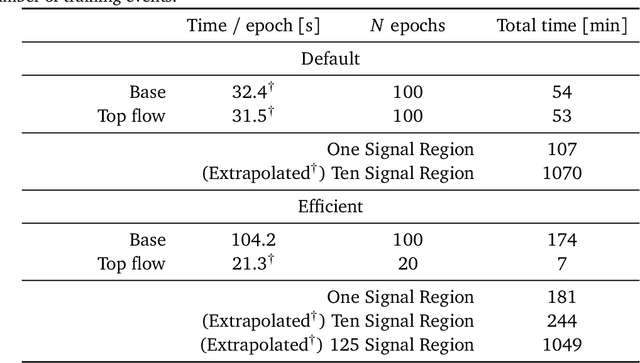
Model independent techniques for constructing background data templates using generative models have shown great promise for use in searches for new physics processes at the LHC. We introduce a major improvement to the CURTAINs method by training the conditional normalizing flow between two side-band regions using maximum likelihood estimation instead of an optimal transport loss. The new training objective improves the robustness and fidelity of the transformed data and is much faster and easier to train. We compare the performance against the previous approach and the current state of the art using the LHC Olympics anomaly detection dataset, where we see a significant improvement in sensitivity over the original CURTAINs method. Furthermore, CURTAINsF4F requires substantially less computational resources to cover a large number of signal regions than other fully data driven approaches. When using an efficient configuration, an order of magnitude more models can be trained in the same time required for ten signal regions, without a significant drop in performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge