Curriculum based Dropout Discriminator for Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
Jul 24, 2019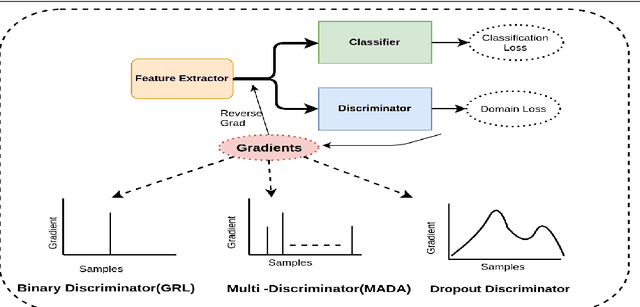
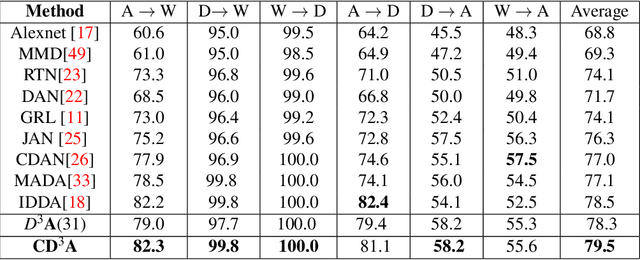
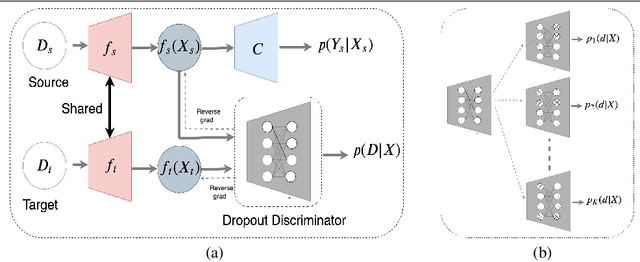
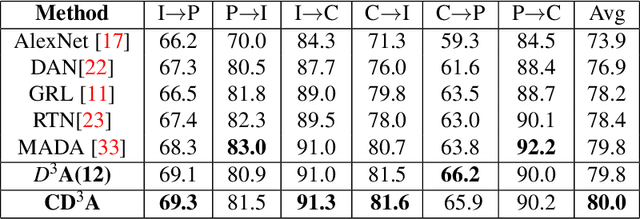
Domain adaptation is essential to enable wide usage of deep learning based networks trained using large labeled datasets. Adversarial learning based techniques have shown their utility towards solving this problem using a discriminator that ensures source and target distributions are close. However, here we suggest that rather than using a point estimate, it would be useful if a distribution based discriminator could be used to bridge this gap. This could be achieved using multiple classifiers or using traditional ensemble methods. In contrast, we suggest that a Monte Carlo dropout based ensemble discriminator could suffice to obtain the distribution based discriminator. Specifically, we propose a curriculum based dropout discriminator that gradually increases the variance of the sample based distribution and the corresponding reverse gradients are used to align the source and target feature representations. The detailed results and thorough ablation analysis show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge