Current Advances in Computational Lung Ultrasound Imaging: A Review
Paper and Code
Mar 23, 2021
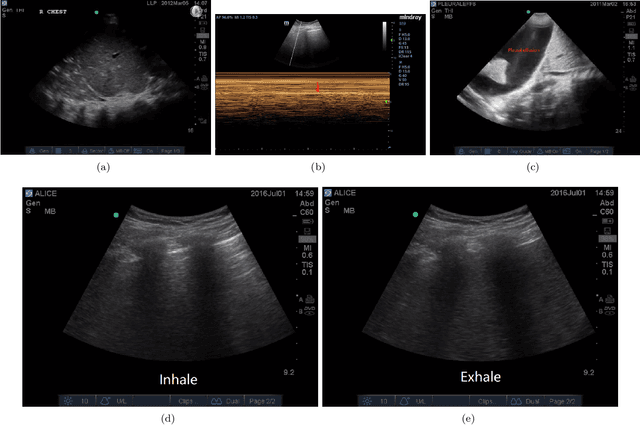
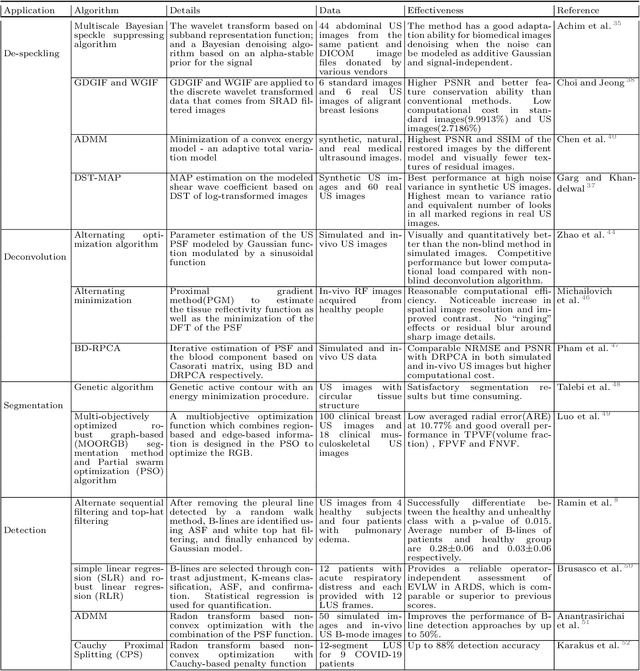

In the field of biomedical imaging, ultrasonography has become increasingly widespread, and an important auxiliary diagnostic tool with unique advantages, such as being non-ionising and often portable. This article reviews the state-of-the-art in medical ultrasound image computing and in particular its application in the examination of the lungs. First, we review the current developments in medical ultrasound technology. We then focus on the characteristics of lung ultrasonography and on its ability to diagnose a variety of diseases through the identification of various artefacts. We review medical ultrasound image processing methods by splitting them into two categories: (1) traditional model-based methods, and (2) data driven methods. For the former, we consider inverse problem based methods by focusing in particular on ultrasound image despeckling, deconvolution, and line artefacts detection. Among the data-driven approaches, we discuss various works based on deep/machine learning, which include various effective network architectures implementing supervised, weakly supervised and unsupervised learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge