Cross-spectral Face Completion for NIR-VIS Heterogeneous Face Recognition
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2019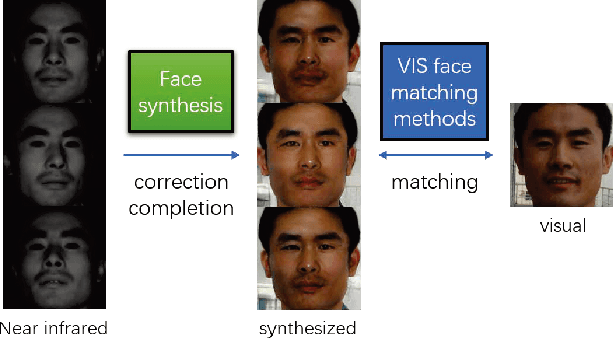
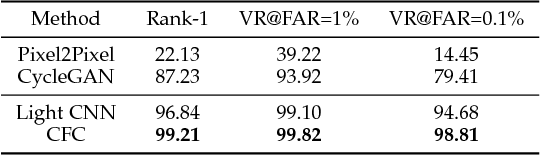
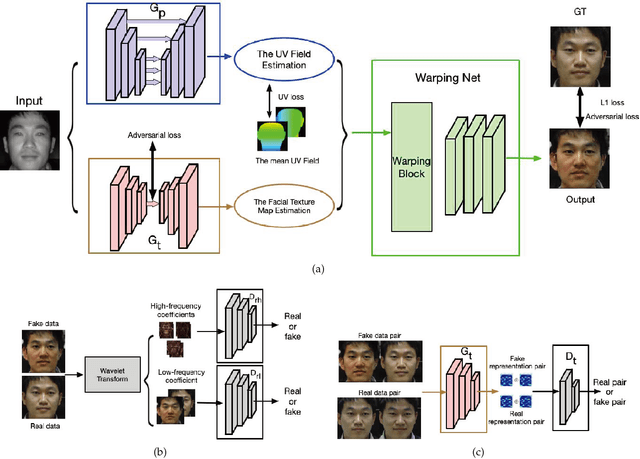
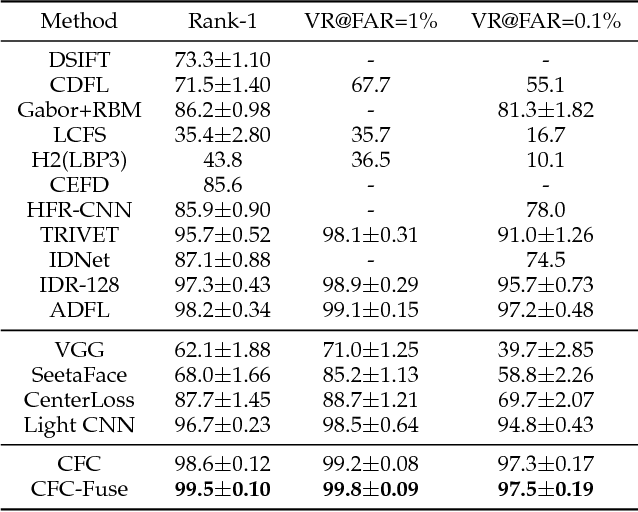
Near infrared-visible (NIR-VIS) heterogeneous face recognition refers to the process of matching NIR to VIS face images. Current heterogeneous methods try to extend VIS face recognition methods to the NIR spectrum by synthesizing VIS images from NIR images. However, due to self-occlusion and sensing gap, NIR face images lose some visible lighting contents so that they are always incomplete compared to VIS face images. This paper models high resolution heterogeneous face synthesis as a complementary combination of two components, a texture inpainting component and pose correction component. The inpainting component synthesizes and inpaints VIS image textures from NIR image textures. The correction component maps any pose in NIR images to a frontal pose in VIS images, resulting in paired NIR and VIS textures. A warping procedure is developed to integrate the two components into an end-to-end deep network. A fine-grained discriminator and a wavelet-based discriminator are designed to supervise intra-class variance and visual quality respectively. One UV loss, two adversarial losses and one pixel loss are imposed to ensure synthesis results. We demonstrate that by attaching the correction component, we can simplify heterogeneous face synthesis from one-to-many unpaired image translation to one-to-one paired image translation, and minimize spectral and pose discrepancy during heterogeneous recognition. Extensive experimental results show that our network not only generates high-resolution VIS face images and but also facilitates the accuracy improvement of heterogeneous face recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge