Cross-Lingual Transfer Learning for Complex Word Identification
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2020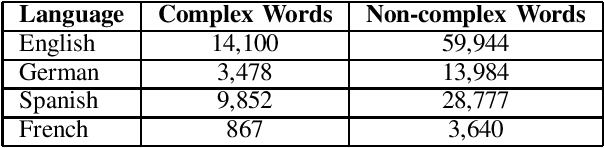
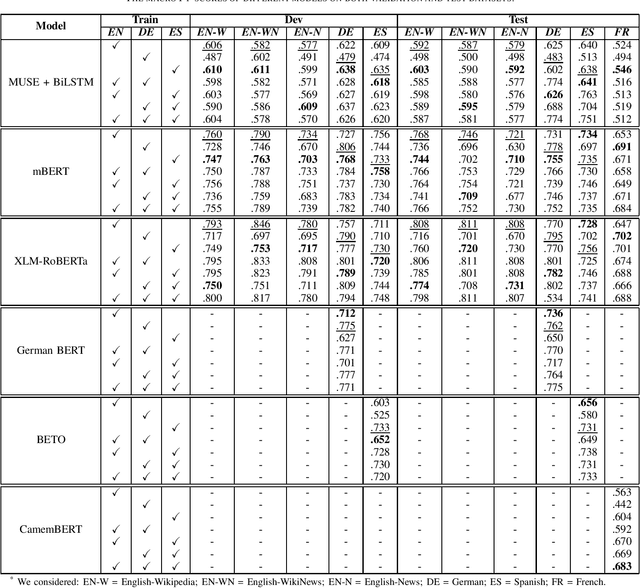
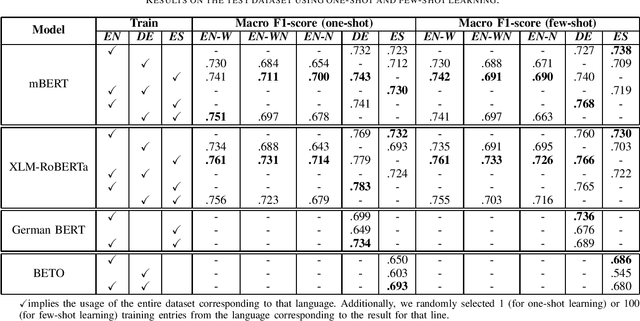
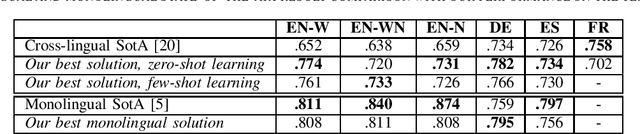
Complex Word Identification (CWI) is a task centered on detecting hard-to-understand words, or groups of words, in texts from different areas of expertise. The purpose of CWI is to highlight problematic structures that non-native speakers would usually find difficult to understand. Our approach uses zero-shot, one-shot, and few-shot learning techniques, alongside state-of-the-art solutions for Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks (i.e., Transformers). Our aim is to provide evidence that the proposed models can learn the characteristics of complex words in a multilingual environment by relying on the CWI shared task 2018 dataset available for four different languages (i.e., English, German, Spanish, and also French). Our approach surpasses state-of-the-art cross-lingual results in terms of macro F1-score on English (0.774), German (0.782), and Spanish (0.734) languages, for the zero-shot learning scenario. At the same time, our model also outperforms the state-of-the-art monolingual result for German (0.795 macro F1-score).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge