Cross-Lingual Task-Specific Representation Learning for Text Classification in Resource Poor Languages
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2018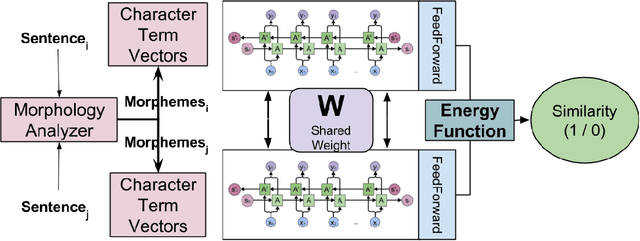
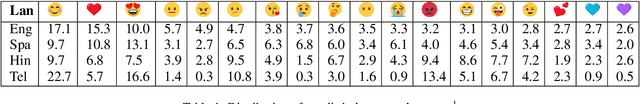

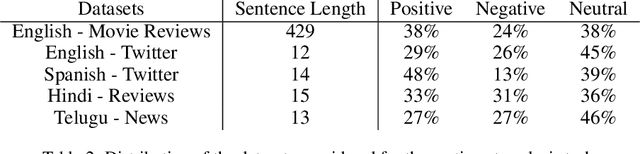
Neural network models have shown promising results for text classification. However, these solutions are limited by their dependence on the availability of annotated data. The prospect of leveraging resource-rich languages to enhance the text classification of resource-poor languages is fascinating. The performance on resource-poor languages can significantly improve if the resource availability constraints can be offset. To this end, we present a twin Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) network with shared parameters consolidated by a contrastive loss function (based on a similarity metric). The model learns the representation of resource-poor and resource-rich sentences in a common space by using the similarity between their assigned annotation tags. Hence, the model projects sentences with similar tags closer and those with different tags farther from each other. We evaluated our model on the classification tasks of sentiment analysis and emoji prediction for resource-poor languages - Hindi and Telugu and resource-rich languages - English and Spanish. Our model significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in both the tasks across all metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge