Creating Artificial Students that Never Existed: Leveraging Large Language Models and CTGANs for Synthetic Data Generation
Paper and Code
Jan 03, 2025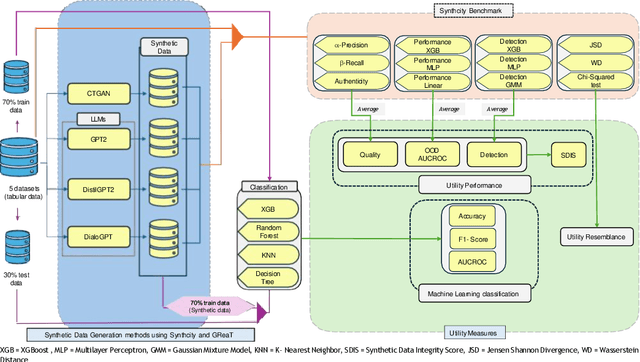
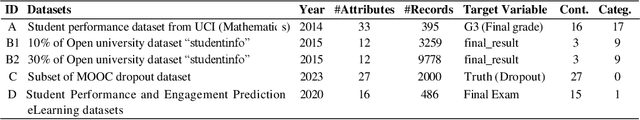
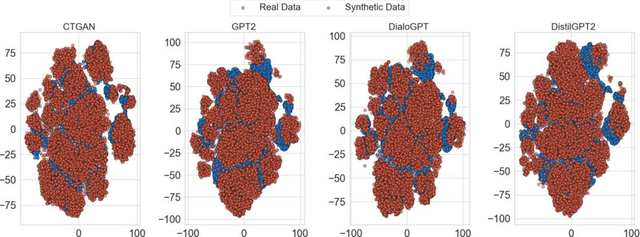
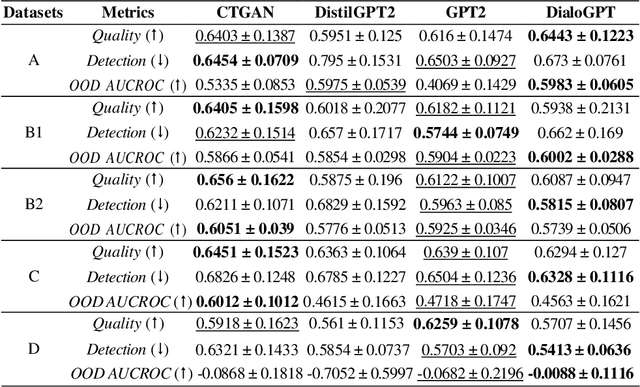
In this study, we explore the growing potential of AI and deep learning technologies, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Large Language Models (LLMs), for generating synthetic tabular data. Access to quality students data is critical for advancing learning analytics, but privacy concerns and stricter data protection regulations worldwide limit their availability and usage. Synthetic data offers a promising alternative. We investigate whether synthetic data can be leveraged to create artificial students for serving learning analytics models. Using the popular GAN model CTGAN and three LLMs- GPT2, DistilGPT2, and DialoGPT, we generate synthetic tabular student data. Our results demonstrate the strong potential of these methods to produce high-quality synthetic datasets that resemble real students data. To validate our findings, we apply a comprehensive set of utility evaluation metrics to assess the statistical and predictive performance of the synthetic data and compare the different generator models used, specially the performance of LLMs. Our study aims to provide the learning analytics community with valuable insights into the use of synthetic data, laying the groundwork for expanding the field methodological toolbox with new innovative approaches for learning analytics data generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge