Core and Periphery as Closed-System Precepts for Engineering General Intelligence
Paper and Code
Aug 04, 2022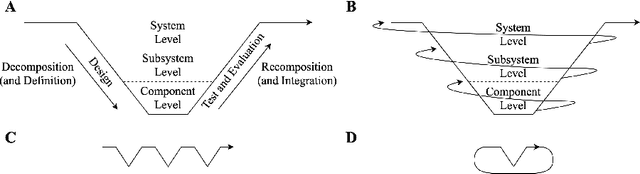
Engineering methods are centered around traditional notions of decomposition and recomposition that rely on partitioning the inputs and outputs of components to allow for component-level properties to hold after their composition. In artificial intelligence (AI), however, systems are often expected to influence their environments, and, by way of their environments, to influence themselves. Thus, it is unclear if an AI system's inputs will be independent of its outputs, and, therefore, if AI systems can be treated as traditional components. This paper posits that engineering general intelligence requires new general systems precepts, termed the core and periphery, and explores their theoretical uses. The new precepts are elaborated using abstract systems theory and the Law of Requisite Variety. By using the presented material, engineers can better understand the general character of regulating the outcomes of AI to achieve stakeholder needs and how the general systems nature of embodiment challenges traditional engineering practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge