Conversational Grounding: Annotation and Analysis of Grounding Acts and Grounding Units
Paper and Code
Mar 25, 2024


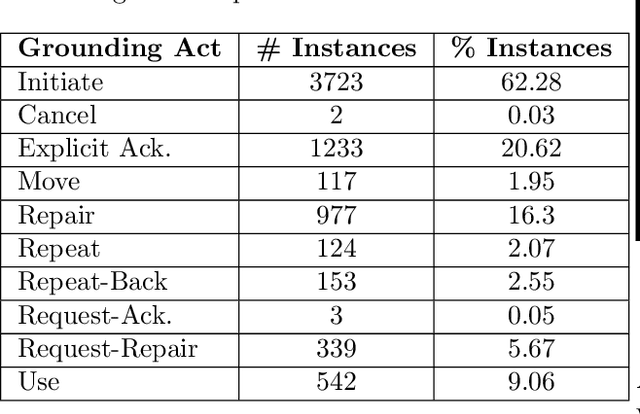
Successful conversations often rest on common understanding, where all parties are on the same page about the information being shared. This process, known as conversational grounding, is crucial for building trustworthy dialog systems that can accurately keep track of and recall the shared information. The proficiencies of an agent in grounding the conveyed information significantly contribute to building a reliable dialog system. Despite recent advancements in dialog systems, there exists a noticeable deficit in their grounding capabilities. Traum provided a framework for conversational grounding introducing Grounding Acts and Grounding Units, but substantial progress, especially in the realm of Large Language Models, remains lacking. To bridge this gap, we present the annotation of two dialog corpora employing Grounding Acts, Grounding Units, and a measure of their degree of grounding. We discuss our key findings during the annotation and also provide a baseline model to test the performance of current Language Models in categorizing the grounding acts of the dialogs. Our work aims to provide a useful resource for further research in making conversations with machines better understood and more reliable in natural day-to-day collaborative dialogs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge