Convergence of Federated Learning over a Noisy Downlink
Paper and Code
Aug 25, 2020
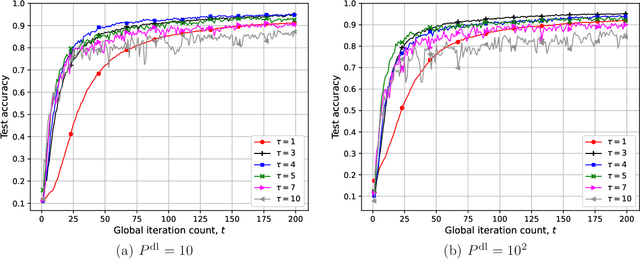
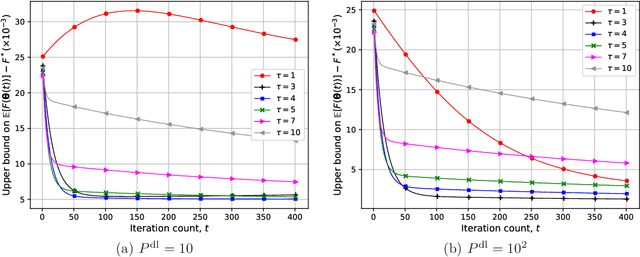
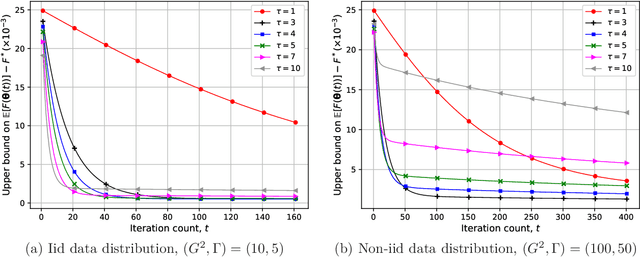
We study federated learning (FL), where power-limited wireless devices utilize their local datasets to collaboratively train a global model with the help of a remote parameter server (PS). The PS has access to the global model and shares it with the devices for local training, and the devices return the result of their local updates to the PS to update the global model. This framework requires downlink transmission from the PS to the devices and uplink transmission from the devices to the PS. The goal of this study is to investigate the impact of the bandwidth-limited shared wireless medium in both the downlink and uplink on the performance of FL with a focus on the downlink. To this end, the downlink and uplink channels are modeled as fading broadcast and multiple access channels, respectively, both with limited bandwidth. For downlink transmission, we first introduce a digital approach, where a quantization technique is employed at the PS to broadcast the global model update at a common rate such that all the devices can decode it. Next, we propose analog downlink transmission, where the global model is broadcast by the PS in an uncoded manner. We consider analog transmission over the uplink in both cases. We further analyze the convergence behavior of the proposed analog approach assuming that the uplink transmission is error-free. Numerical experiments show that the analog downlink approach provides significant improvement over the digital one, despite a significantly lower transmit power at the PS. The experimental results corroborate the convergence results, and show that a smaller number of local iterations should be used when the data distribution is more biased, and also when the devices have a better estimate of the global model in the analog downlink approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge