Contrastive Neural Ratio Estimation
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2022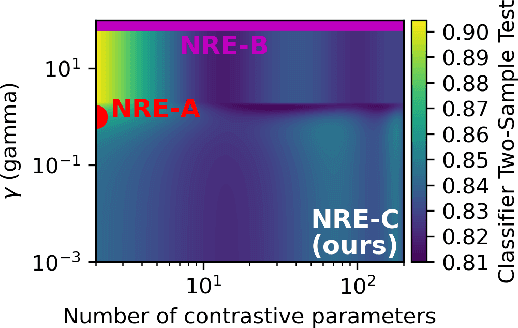
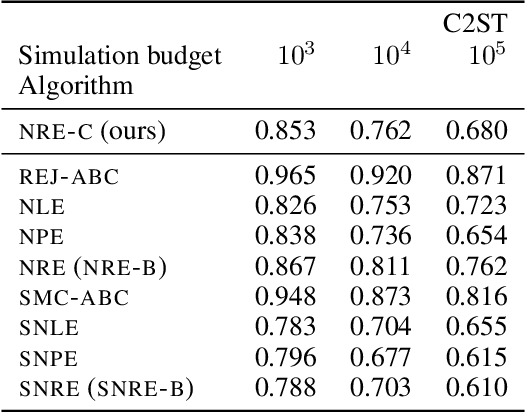
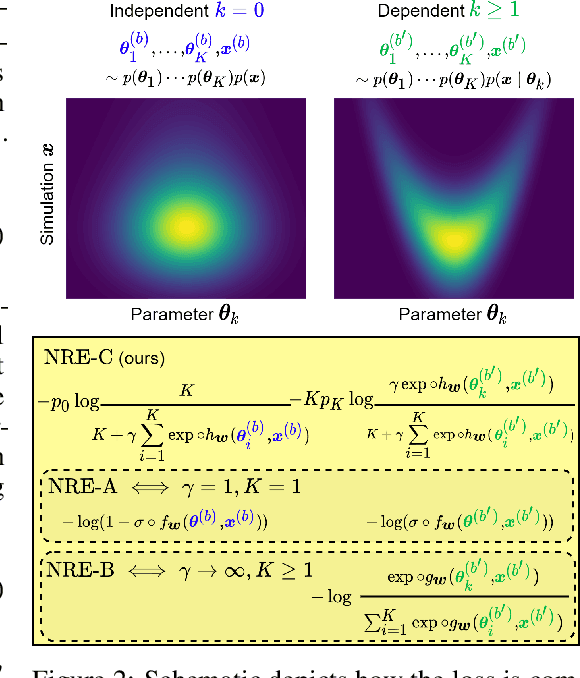
Likelihood-to-evidence ratio estimation is usually cast as either a binary (NRE-A) or a multiclass (NRE-B) classification task. In contrast to the binary classification framework, the current formulation of the multiclass version has an intrinsic and unknown bias term, making otherwise informative diagnostics unreliable. We propose a multiclass framework free from the bias inherent to NRE-B at optimum, leaving us in the position to run diagnostics that practitioners depend on. It also recovers NRE-A in one corner case and NRE-B in the limiting case. For fair comparison, we benchmark the behavior of all algorithms in both familiar and novel training regimes: when jointly drawn data is unlimited, when data is fixed but prior draws are unlimited, and in the commonplace fixed data and parameters setting. Our investigations reveal that the highest performing models are distant from the competitors (NRE-A, NRE-B) in hyperparameter space. We make a recommendation for hyperparameters distinct from the previous models. We suggest a bound on the mutual information as a performance metric for simulation-based inference methods, without the need for posterior samples, and provide experimental results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge