Contextual Motifs: Increasing the Utility of Motifs using Contextual Data
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2017
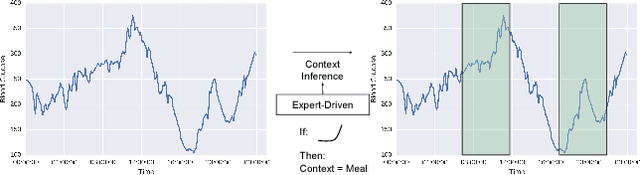
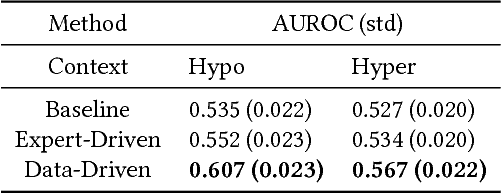
Motifs are a powerful tool for analyzing physiological waveform data. Standard motif methods, however, ignore important contextual information (e.g., what the patient was doing at the time the data were collected). We hypothesize that these additional contextual data could increase the utility of motifs. Thus, we propose an extension to motifs, contextual motifs, that incorporates context. Recognizing that, oftentimes, context may be unobserved or unavailable, we focus on methods to jointly infer motifs and context. Applied to both simulated and real physiological data, our proposed approach improves upon existing motif methods in terms of the discriminative utility of the discovered motifs. In particular, we discovered contextual motifs in continuous glucose monitor (CGM) data collected from patients with type 1 diabetes. Compared to their contextless counterparts, these contextual motifs led to better predictions of hypo- and hyperglycemic events. Our results suggest that even when inferred, context is useful in both a long- and short-term prediction horizon when processing and interpreting physiological waveform data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge