Context Model for Pedestrian Intention Prediction using Factored Latent-Dynamic Conditional Random Fields
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2019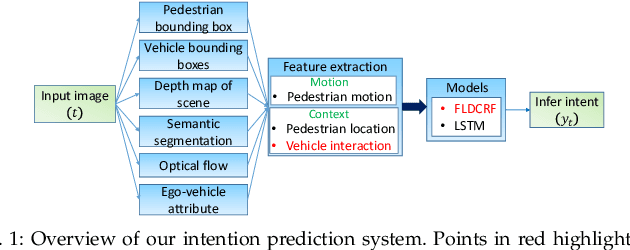
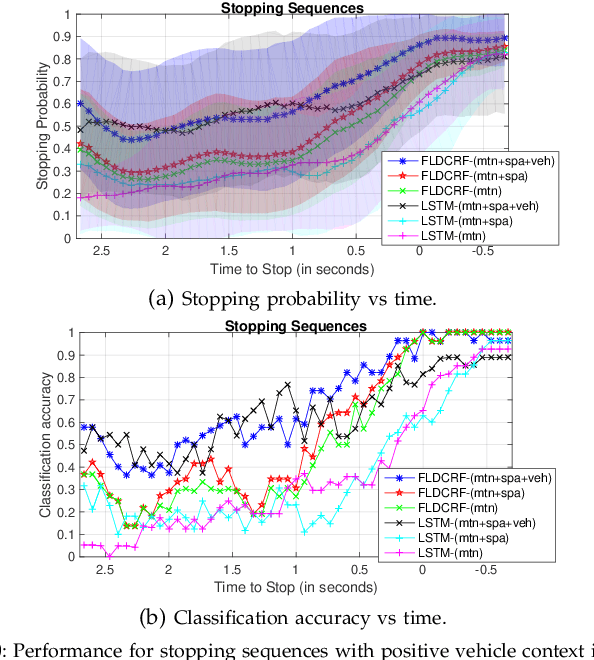

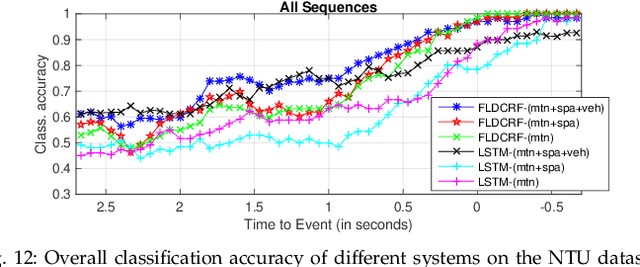
Smooth handling of pedestrian interactions is a key requirement for Autonomous Vehicles (AV) and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). Such systems call for early and accurate prediction of a pedestrian's crossing/not-crossing behaviour in front of the vehicle. Existing approaches to pedestrian behaviour prediction make use of pedestrian motion, his/her location in a scene and static context variables such as traffic lights, zebra crossings etc. We stress on the necessity of early prediction for smooth operation of such systems. We introduce the influence of vehicle interactions on pedestrian intention for this purpose. In this paper, we show a discernible advance in prediction time aided by the inclusion of such vehicle interaction context. We apply our methods to two different datasets, one in-house collected - NTU dataset and another public real-life benchmark - JAAD dataset. We also propose a generic graphical model Factored Latent-Dynamic Conditional Random Fields (FLDCRF) for single and multi-label sequence prediction as well as joint interaction modeling tasks. FLDCRF outperforms Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks across the datasets ($\sim$100 sequences per dataset) over identical time-series features. While the existing best system predicts pedestrian stopping behaviour with 70\% accuracy 0.38 seconds before the actual events, our system achieves such accuracy at least 0.9 seconds on an average before the actual events across datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge