Contact modelling and tactile data processing for robot skin
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2018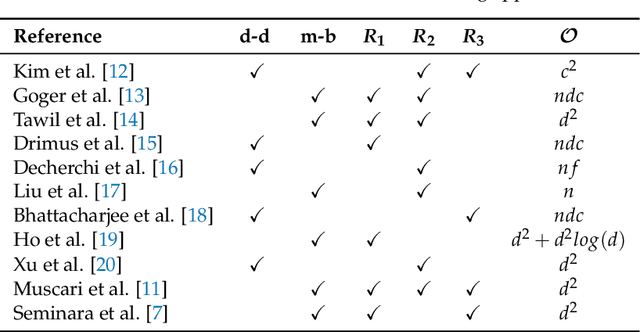
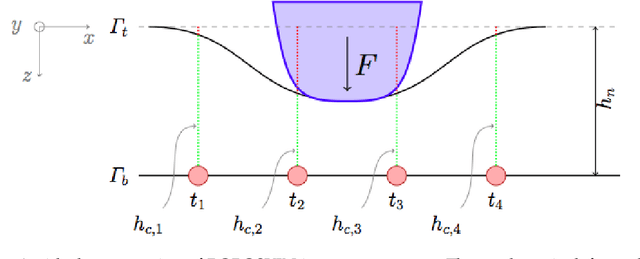
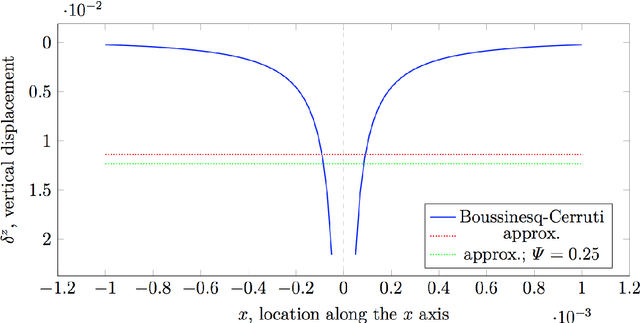
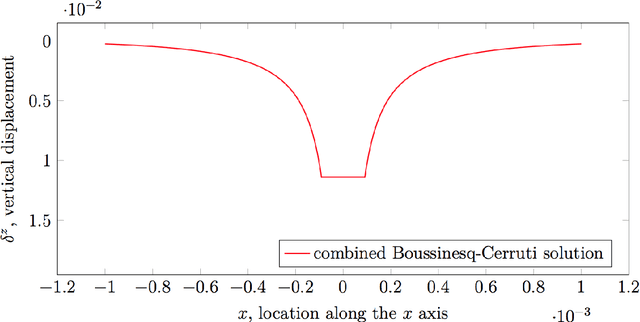
Tactile sensing is a key enabling technology to develop complex behaviours for robots interacting with humans or the environment. This paper discusses computational aspects playing a significant role when extracting information about contact events. Considering a large-scale, capacitance-based robot skin technology we developed in the past few years, we analyse the classical Boussinesq-Cerruti's solution and the Love's approach for solving a distributed inverse contact problem, both from a qualitative and a computational perspective. Our contribution is the characterisation of algorithms performance using a freely available dataset and data originating from surfaces provided with robot skin.
* Submitted to Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge