Constrained Posterior Sampling: Time Series Generation with Hard Constraints
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2024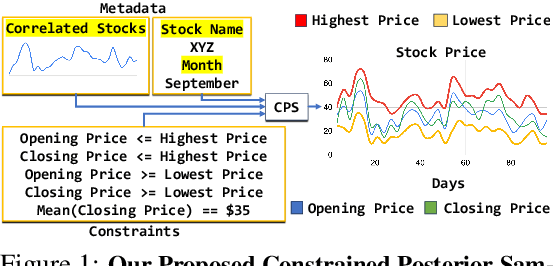
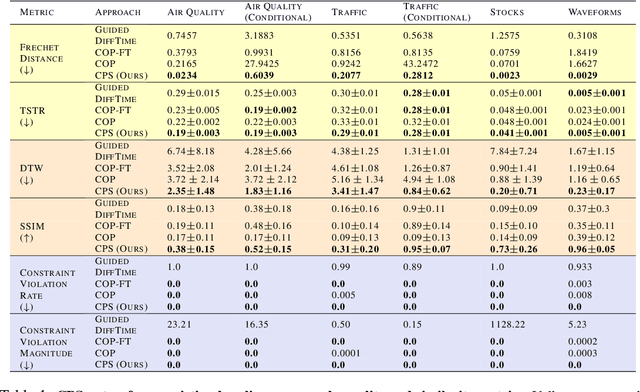
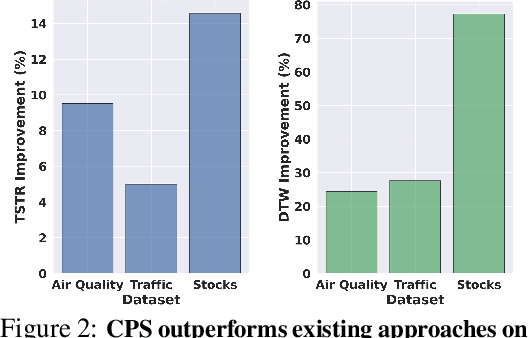

Generating realistic time series samples is crucial for stress-testing models and protecting user privacy by using synthetic data. In engineering and safety-critical applications, these samples must meet certain hard constraints that are domain-specific or naturally imposed by physics or nature. Consider, for example, generating electricity demand patterns with constraints on peak demand times. This can be used to stress-test the functioning of power grids during adverse weather conditions. Existing approaches for generating constrained time series are either not scalable or degrade sample quality. To address these challenges, we introduce Constrained Posterior Sampling (CPS), a diffusion-based sampling algorithm that aims to project the posterior mean estimate into the constraint set after each denoising update. Notably, CPS scales to a large number of constraints (~100) without requiring additional training. We provide theoretical justifications highlighting the impact of our projection step on sampling. Empirically, CPS outperforms state-of-the-art methods in sample quality and similarity to real time series by around 10% and 42%, respectively, on real-world stocks, traffic, and air quality datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge