Conformalized Teleoperation: Confidently Mapping Human Inputs to High-Dimensional Robot Actions
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2024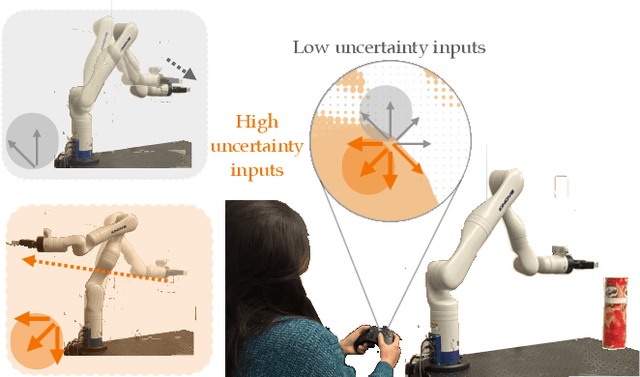
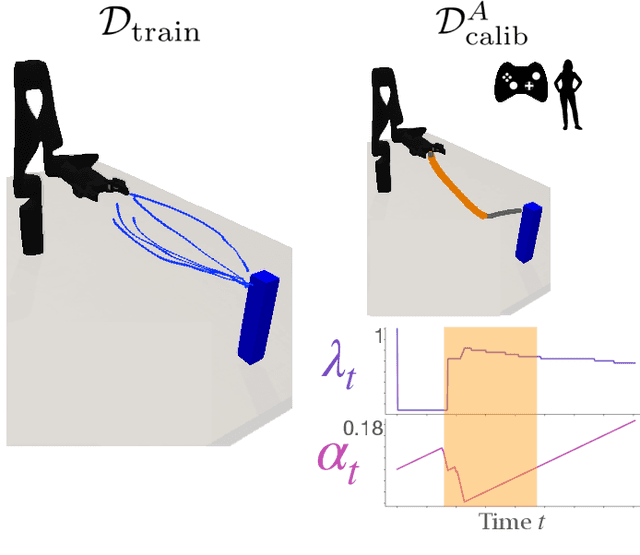
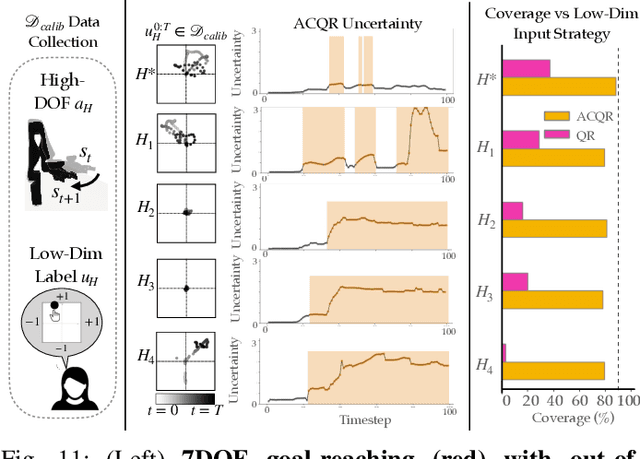
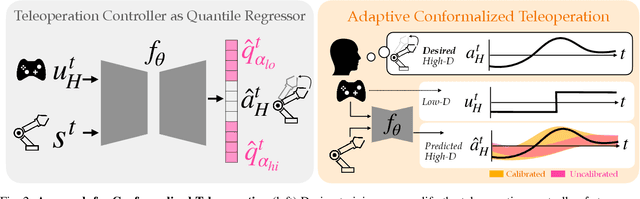
Assistive robotic arms often have more degrees-of-freedom than a human teleoperator can control with a low-dimensional input, like a joystick. To overcome this challenge, existing approaches use data-driven methods to learn a mapping from low-dimensional human inputs to high-dimensional robot actions. However, determining if such a black-box mapping can confidently infer a user's intended high-dimensional action from low-dimensional inputs remains an open problem. Our key idea is to adapt the assistive map at training time to additionally estimate high-dimensional action quantiles, and then calibrate these quantiles via rigorous uncertainty quantification methods. Specifically, we leverage adaptive conformal prediction which adjusts the intervals over time, reducing the uncertainty bounds when the mapping is performant and increasing the bounds when the mapping consistently mis-predicts. Furthermore, we propose an uncertainty-interval-based mechanism for detecting high-uncertainty user inputs and robot states. We evaluate the efficacy of our proposed approach in a 2D assistive navigation task and two 7DOF Kinova Jaco tasks involving assistive cup grasping and goal reaching. Our findings demonstrate that conformalized assistive teleoperation manages to detect (but not differentiate between) high uncertainty induced by diverse preferences and induced by low-precision trajectories in the mapping's training dataset. On the whole, we see this work as a key step towards enabling robots to quantify their own uncertainty and proactively seek intervention when needed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge