Computing Optimal Assignments in Linear Time for Graph Matching
Paper and Code
Jan 29, 2019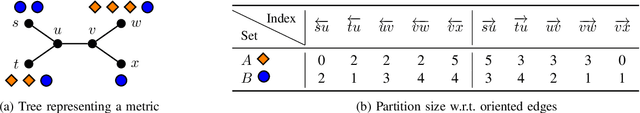
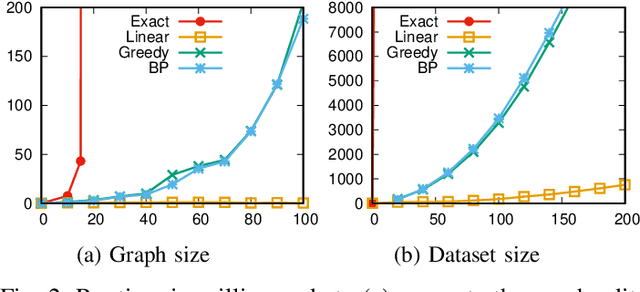
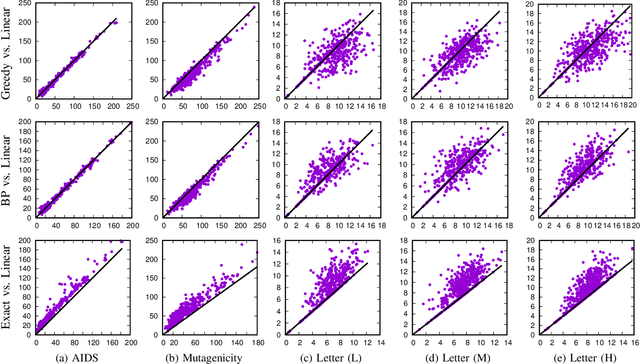
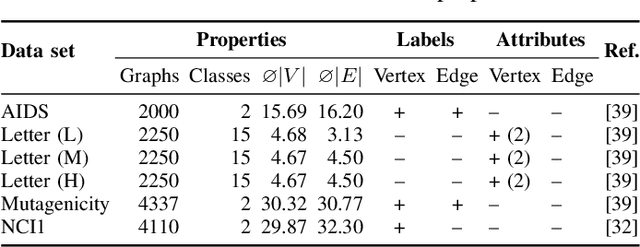
Finding an optimal assignment between two sets of objects is a fundamental problem arising in many applications, including the matching of `bag-of-words' representations in natural language processing and computer vision. Solving the assignment problem typically requires cubic time and its pairwise computation is expensive on large datasets. In this paper, we develop an algorithm which can find an optimal assignment in linear time when the cost function between objects is represented by a tree distance. We employ the method to approximate the edit distance between two graphs by matching their vertices in linear time. To this end, we propose two tree distances, the first of which reflects discrete and structural differences between vertices, and the second of which can be used to compare continuous labels. We verify the effectiveness and efficiency of our methods using synthetic and real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge