Compressive Summarization with Plausibility and Salience Modeling
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2020
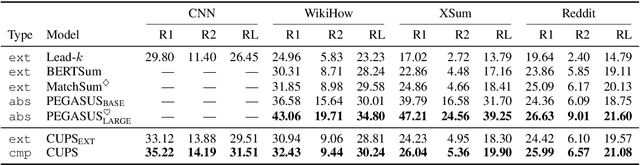
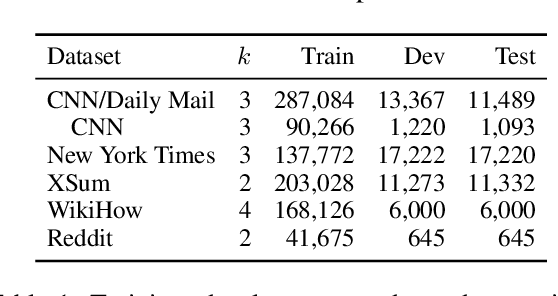
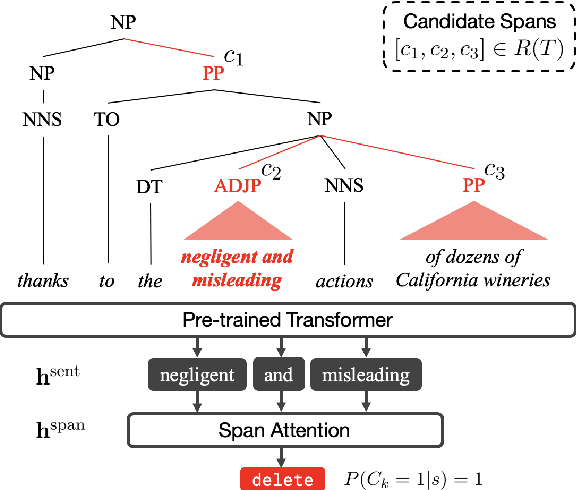
Compressive summarization systems typically rely on a crafted set of syntactic rules to determine what spans of possible summary sentences can be deleted, then learn a model of what to actually delete by optimizing for content selection (ROUGE). In this work, we propose to relax the rigid syntactic constraints on candidate spans and instead leave compression decisions to two data-driven criteria: plausibility and salience. Deleting a span is plausible if removing it maintains the grammaticality and factuality of a sentence, and spans are salient if they contain important information from the summary. Each of these is judged by a pre-trained Transformer model, and only deletions that are both plausible and not salient can be applied. When integrated into a simple extraction-compression pipeline, our method achieves strong in-domain results on benchmark summarization datasets, and human evaluation shows that the plausibility model generally selects for grammatical and factual deletions. Furthermore, the flexibility of our approach allows it to generalize cross-domain: our system fine-tuned on only 500 samples from a new domain can match or exceed an in-domain extractive model trained on much more data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge