Comparison-based Conversational Recommender System with Relative Bandit Feedback
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2022
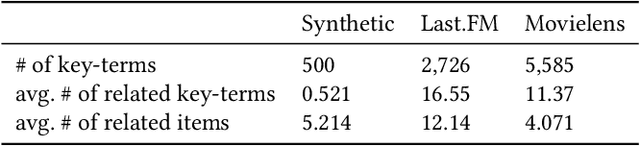

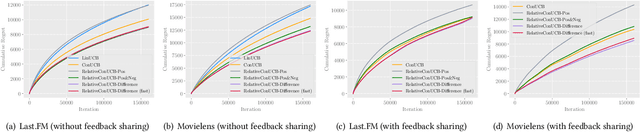
With the recent advances of conversational recommendations, the recommender system is able to actively and dynamically elicit user preference via conversational interactions. To achieve this, the system periodically queries users' preference on attributes and collects their feedback. However, most existing conversational recommender systems only enable the user to provide absolute feedback to the attributes. In practice, the absolute feedback is usually limited, as the users tend to provide biased feedback when expressing the preference. Instead, the user is often more inclined to express comparative preferences, since user preferences are inherently relative. To enable users to provide comparative preferences during conversational interactions, we propose a novel comparison-based conversational recommender system. The relative feedback, though more practical, is not easy to be incorporated since its feedback scale is always mismatched with users' absolute preferences. With effectively collecting and understanding the relative feedback from an interactive manner, we further propose a new bandit algorithm, which we call RelativeConUCB. The experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets validate the advantage of our proposed method, compared to the existing bandit algorithms in the conversational recommender systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge