Combining Hybrid Architecture and Pseudo-label for Semi-supervised Abdominal Organ Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jul 23, 2022
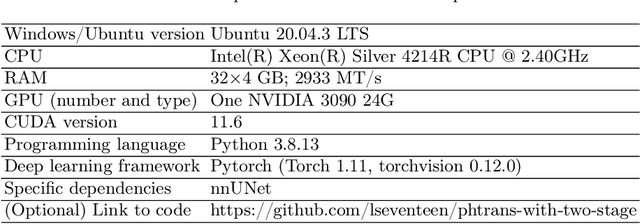
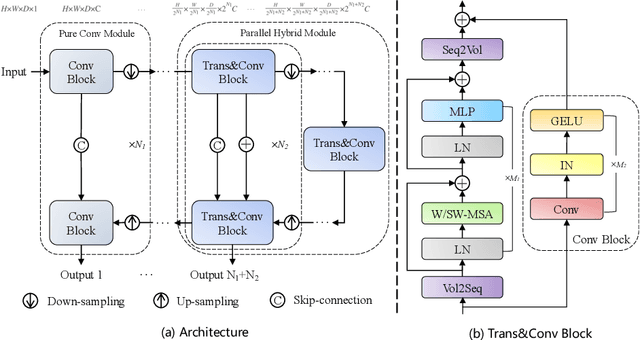
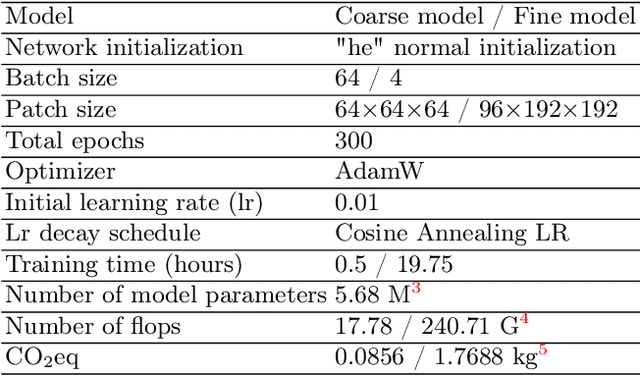
Abdominal organ segmentation has many important clinical applications, such as organ quantification, surgical planning, and disease diagnosis. However, manually annotating organs from CT scans is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Semi-supervised learning has shown the potential to alleviate this challenge by learning from a large set of unlabeled images and limited labeled samples. In this work, we follow the self-training strategy and employ a hybrid architecture (PHTrans) with CNN and Transformer for both teacher and student models to generate precise pseudo-labels. Afterward, we introduce them with label data together into a two-stage segmentation framework with lightweight PHTrans for training to improve the performance and generalization ability of the model while remaining efficient. Experiments on the validation set of FLARE2022 demonstrate that our method achieves excellent segmentation performance as well as fast and low-resource model inference. The average DSC and HSD are 0.8956 and 0.9316, respectively. Under our development environments, the average inference time is 18.62 s, the average maximum GPU memory is 1995.04 MB, and the area under the GPU memory-time curve and the average area under the CPU utilization-time curve are 23196.84 and 319.67.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge