Combined Registration and Fusion of Evidential Occupancy Grid Maps for Live Digital Twins of Traffic
Paper and Code
Apr 07, 2023


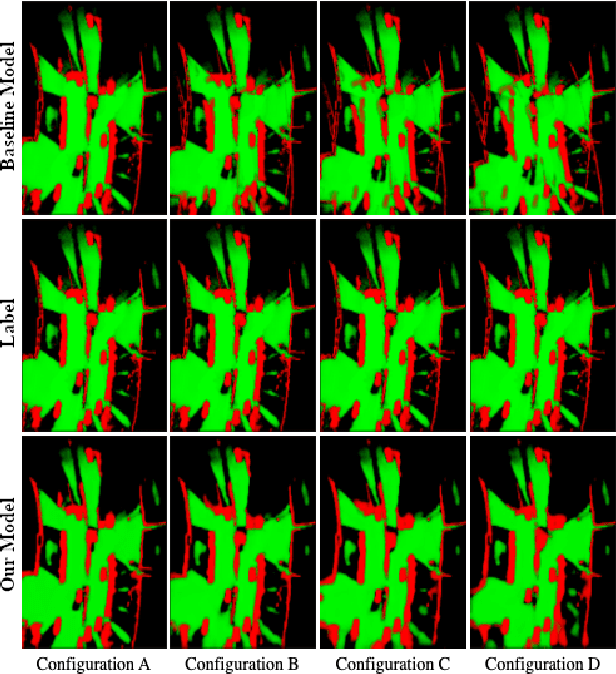
Cooperation of automated vehicles (AVs) can improve safety, efficiency and comfort in traffic. Digital twins of Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C-ITS) play an important role in monitoring, managing and improving traffic. Computing a live digital twin of traffic requires as input live perception data of preferably multiple connected entities such as automated vehicles (AVs). One such type of perception data are evidential occupancy grid maps (OGMs). The computation of a digital twin involves their spatiotemporal alignment and fusion. In this work, we focus on the spatial alignment, also known as registration, and fusion of evidential occupancy grid maps of multiple automated vehicles. While there exists extensive research on the synchronization and fusion of object-based environment representations, the registration and fusion of OGMs originating from multiple connected vehicles has not been investigated much. We propose a methodology that involves training a deep neural network (DNN) to predict a fused evidential OGM from two OGMs computed by different AVs. The output includes an estimate of the first- and second-order uncertainty. We demonstrate that the DNN trained with synthetic data only outperforms a baseline approach based on coordinate transformation and combination rules also on real-world data. Experimental results on synthetic data show that our approach is able to compensate for spatial misalignments of up to 5 meters and 20 degrees.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge