Cogni-Net: Cognitive Feature Learning through Deep Visual Perception
Paper and Code
Nov 01, 2018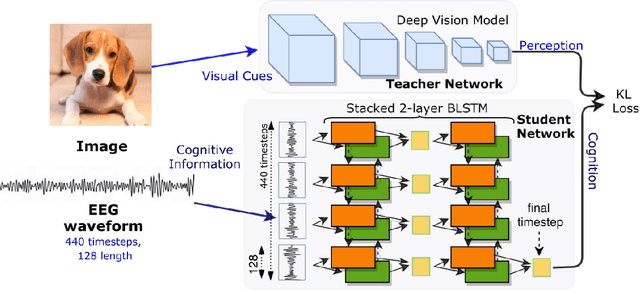
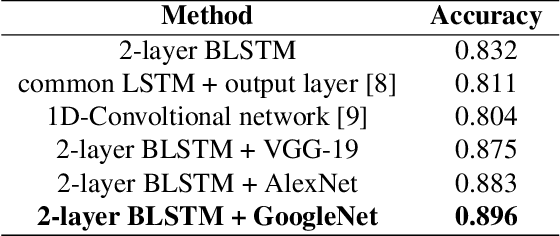
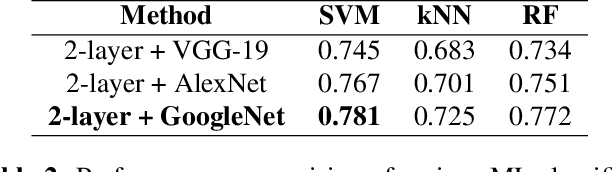
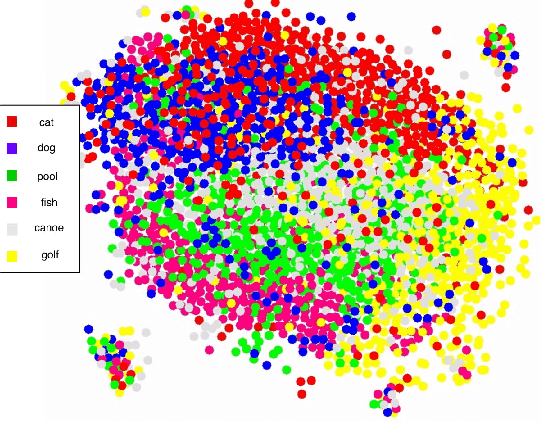
Can we ask computers to recognize what we see from brain signals alone? Our paper seeks to utilize the knowledge learnt in the visual domain by popular pre-trained vision models and use it to teach a recurrent model being trained on brain signals to learn a discriminative manifold of the human brain's cognition of different visual object categories in response to perceived visual cues. For this we make use of brain EEG signals triggered from visual stimuli like images and leverage the natural synchronization between images and their corresponding brain signals to learn a novel representation of the cognitive feature space. The concept of knowledge distillation has been used here for training the deep cognition model, CogniNet\footnote{The source code of the proposed system is publicly available at {https://www.github.com/53X/CogniNET}}, by employing a student-teacher learning technique in order to bridge the process of inter-modal knowledge transfer. The proposed novel architecture obtains state-of-the-art results, significantly surpassing other existing models. The experiments performed by us also suggest that if visual stimuli information like brain EEG signals can be gathered on a large scale, then that would help to obtain a better understanding of the largely unexplored domain of human brain cognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge