CNN Feature boosted SeqSLAM for Real-Time Loop Closure Detection
Paper and Code
Apr 17, 2017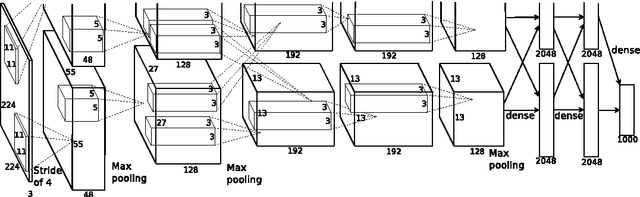
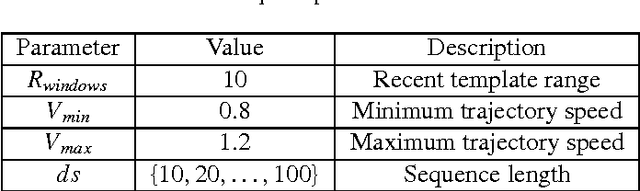

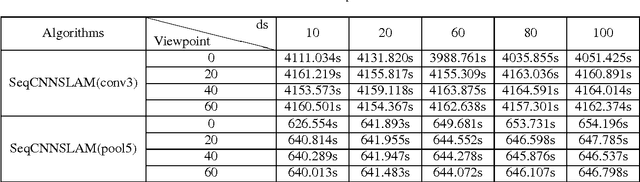
Loop closure detection (LCD) is an indispensable part of simultaneous localization and mapping systems (SLAM); it enables robots to produce a consistent map by recognizing previously visited places. When robots operate over extended periods, robustness to viewpoint and condition changes as well as satisfactory real-time performance become essential requirements for a practical LCD system. This paper presents an approach to directly utilize the outputs at the intermediate layer of a pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) as image descriptors. The matching location is determined by matching the image sequences through a method called SeqCNNSLAM. The utility of SeqCNNSLAM is comprehensively evaluated in terms of viewpoint and condition invariance. Experiments show that SeqCNNSLAM outperforms state-of-the-art LCD systems, such as SeqSLAM and Change Removal, in most cases. To allow for the real-time performance of SeqCNNSLAM, an acceleration method, A-SeqCNNSLAM, is established. This method exploits the location relationship between the matching images of adjacent images to reduce the matching range of the current image. Results demonstrate that acceleration of 4-6 is achieved with minimal accuracy degradation, and the method's runtime satisfies the real-time demand. To extend the applicability of A-SeqCNNSLAM to new environments, a method called O-SeqCNNSLAM is established for the online adjustment of the parameters of A-SeqCNNSLAM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge