CLIP-guided Source-free Object Detection in Aerial Images
Paper and Code
Jan 10, 2024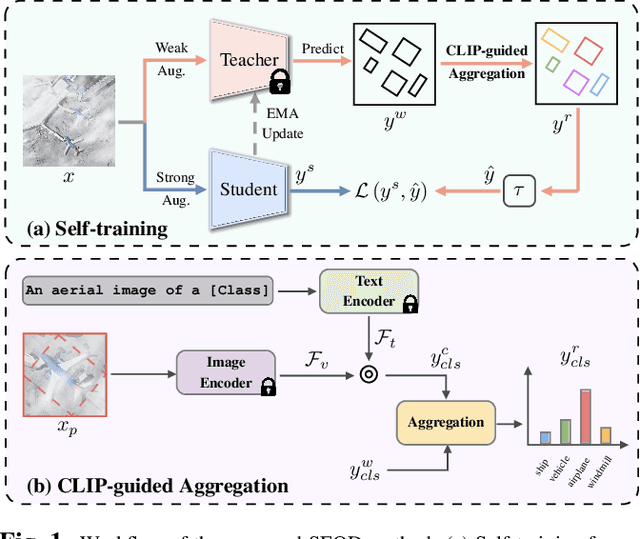
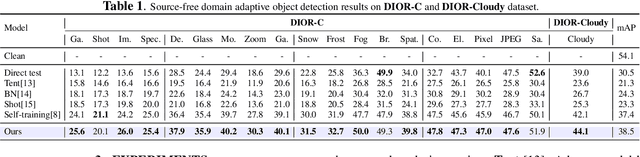
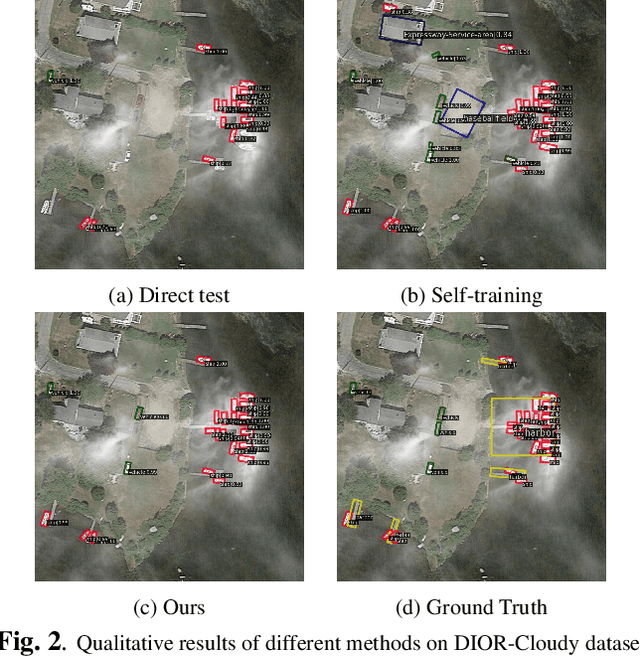
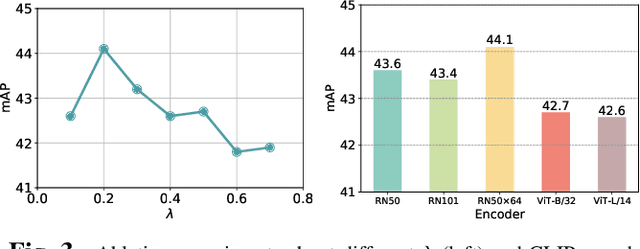
Domain adaptation is crucial in aerial imagery, as the visual representation of these images can significantly vary based on factors such as geographic location, time, and weather conditions. Additionally, high-resolution aerial images often require substantial storage space and may not be readily accessible to the public. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Source-Free Object Detection (SFOD) method. Specifically, our approach is built upon a self-training framework; however, self-training can lead to inaccurate learning in the absence of labeled training data. To address this issue, we further integrate Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) to guide the generation of pseudo-labels, termed CLIP-guided Aggregation. By leveraging CLIP's zero-shot classification capability, we use it to aggregate scores with the original predicted bounding boxes, enabling us to obtain refined scores for the pseudo-labels. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we constructed two new datasets from different domains based on the DIOR dataset, named DIOR-C and DIOR-Cloudy. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms other comparative algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge