Clinician-in-the-Loop Decision Making: Reinforcement Learning with Near-Optimal Set-Valued Policies
Paper and Code
Jul 24, 2020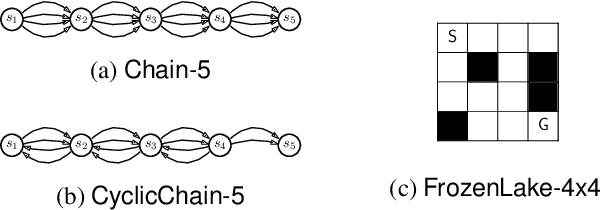
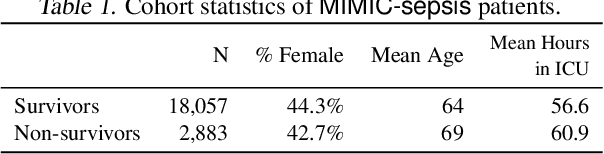
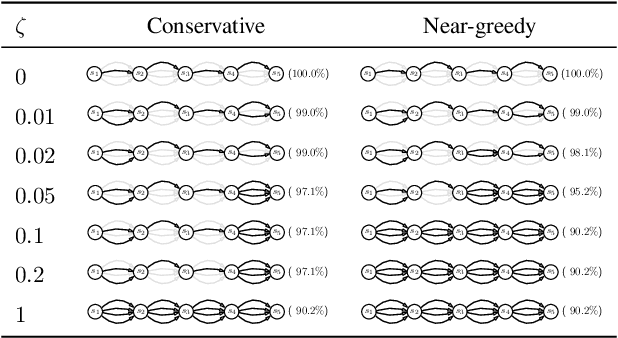
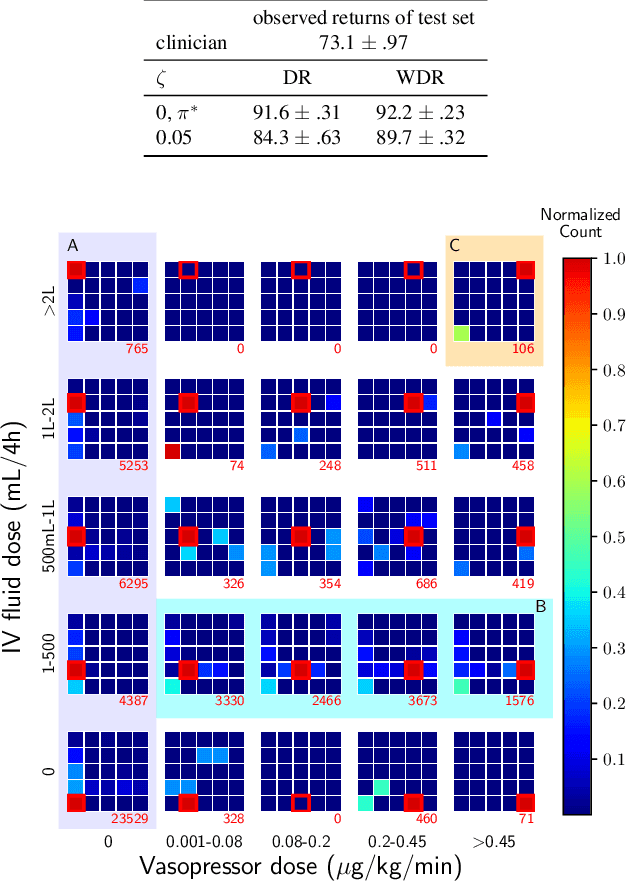
Standard reinforcement learning (RL) aims to find an optimal policy that identifies the best action for each state. However, in healthcare settings, many actions may be near-equivalent with respect to the reward (e.g., survival). We consider an alternative objective -- learning set-valued policies to capture near-equivalent actions that lead to similar cumulative rewards. We propose a model-free algorithm based on temporal difference learning and a near-greedy heuristic for action selection. We analyze the theoretical properties of the proposed algorithm, providing optimality guarantees and demonstrate our approach on simulated environments and a real clinical task. Empirically, the proposed algorithm exhibits good convergence properties and discovers meaningful near-equivalent actions. Our work provides theoretical, as well as practical, foundations for clinician/human-in-the-loop decision making, in which humans (e.g., clinicians, patients) can incorporate additional knowledge (e.g., side effects, patient preference) when selecting among near-equivalent actions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge