Classification with imperfect training labels
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2018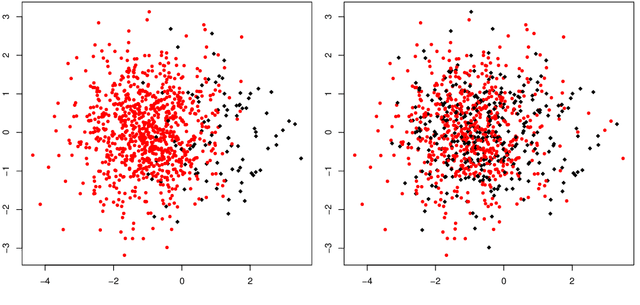
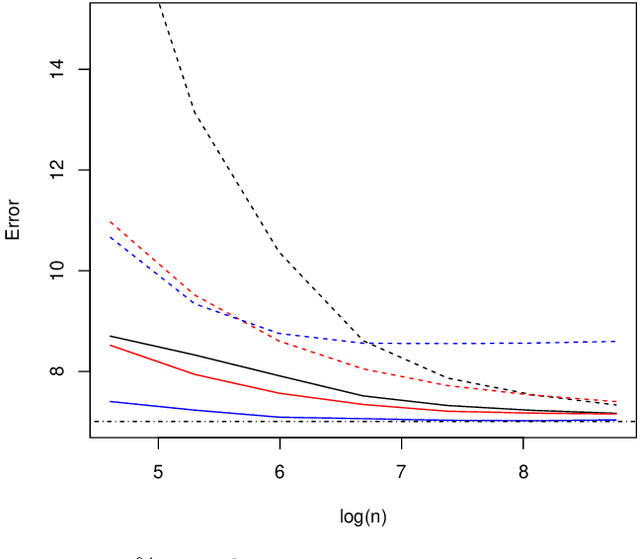
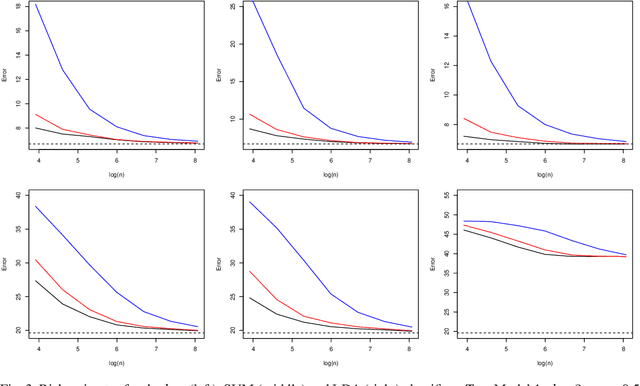
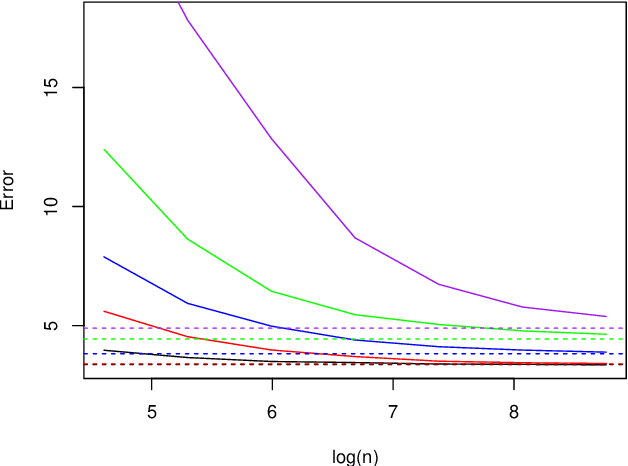
We study the effect of imperfect training data labels on the performance of classification methods. In a general setting, where the probability that an observation in the training dataset is mislabelled may depend on both the feature vector and the true label, we bound the excess risk of an arbitrary classifier trained with imperfect labels in terms of its excess risk for predicting a noisy label. This reveals conditions under which a classifier trained with imperfect labels remains consistent for classifying uncorrupted test data points. Furthermore, under stronger conditions, we derive detailed asymptotic properties for the popular $k$-nearest neighbour ($k$nn), support vector machine (SVM) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) classifiers. One consequence of these results is that the knn and SVM classifiers are robust to imperfect training labels, in the sense that the rate of convergence of the excess risks of these classifiers remains unchanged; in fact, our theoretical and empirical results even show that in some cases, imperfect labels may improve the performance of these methods. On the other hand, the LDA classifier is shown to be typically inconsistent in the presence of label noise unless the prior probabilities of each class are equal. Our theoretical results are supported by a simulation study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge