Classical Out-of-Distribution Detection Methods Benchmark in Text Classification Tasks
Paper and Code
Jul 13, 2023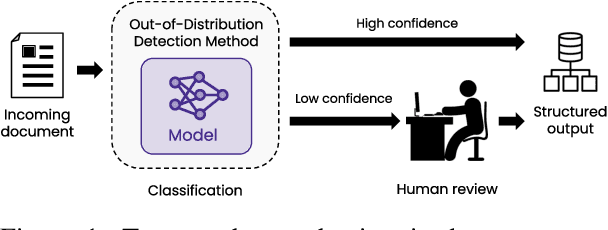
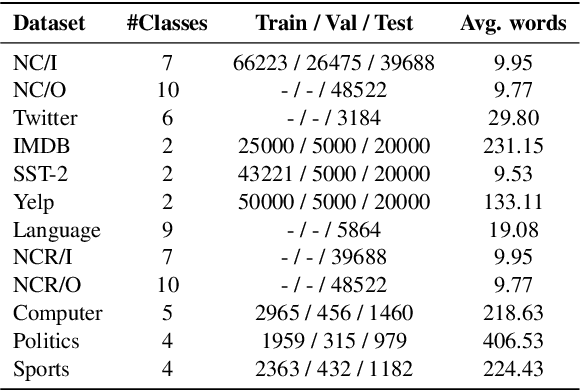
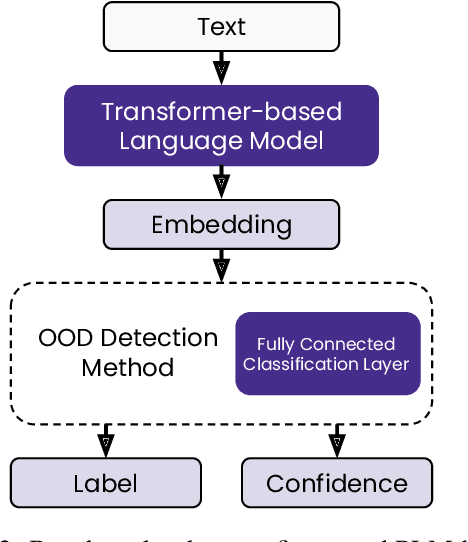
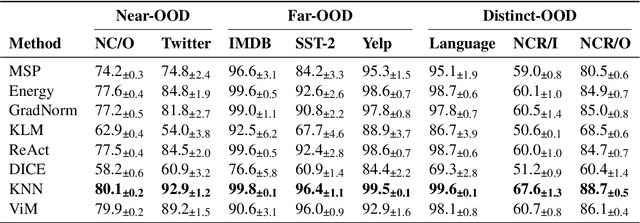
State-of-the-art models can perform well in controlled environments, but they often struggle when presented with out-of-distribution (OOD) examples, making OOD detection a critical component of NLP systems. In this paper, we focus on highlighting the limitations of existing approaches to OOD detection in NLP. Specifically, we evaluated eight OOD detection methods that are easily integrable into existing NLP systems and require no additional OOD data or model modifications. One of our contributions is providing a well-structured research environment that allows for full reproducibility of the results. Additionally, our analysis shows that existing OOD detection methods for NLP tasks are not yet sufficiently sensitive to capture all samples characterized by various types of distributional shifts. Particularly challenging testing scenarios arise in cases of background shift and randomly shuffled word order within in domain texts. This highlights the need for future work to develop more effective OOD detection approaches for the NLP problems, and our work provides a well-defined foundation for further research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge