CHARDA: Causal Hybrid Automata Recovery via Dynamic Analysis
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2017
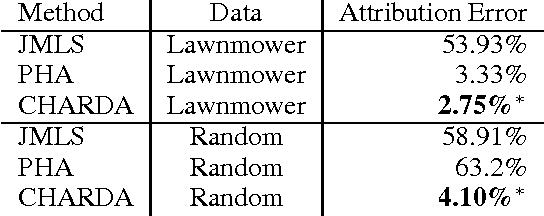

We propose and evaluate a new technique for learning hybrid automata automatically by observing the runtime behavior of a dynamical system. Working from a sequence of continuous state values and predicates about the environment, CHARDA recovers the distinct dynamic modes, learns a model for each mode from a given set of templates, and postulates causal guard conditions which trigger transitions between modes. Our main contribution is the use of information-theoretic measures (1)~as a cost function for data segmentation and model selection to penalize over-fitting and (2)~to determine the likely causes of each transition. CHARDA is easily extended with different classes of model templates, fitting methods, or predicates. In our experiments on a complex videogame character, CHARDA successfully discovers a reasonable over-approximation of the character's true behaviors. Our results also compare favorably against recent work in automatically learning probabilistic timed automata in an aircraft domain: CHARDA exactly learns the modes of these simpler automata.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge