Capture Point Trajectories for Reduced Knee Bend using Step Time Optimization
Paper and Code
Dec 27, 2017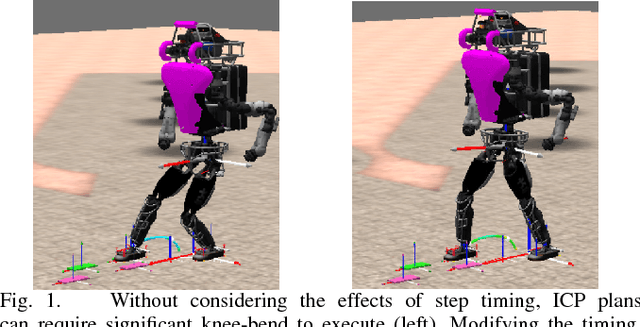
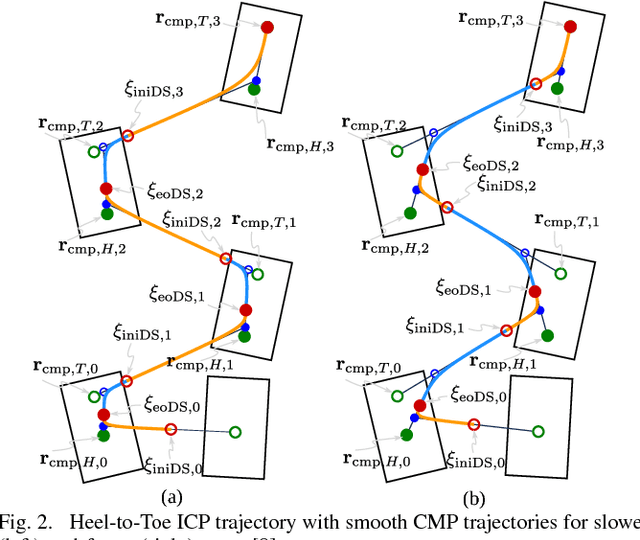
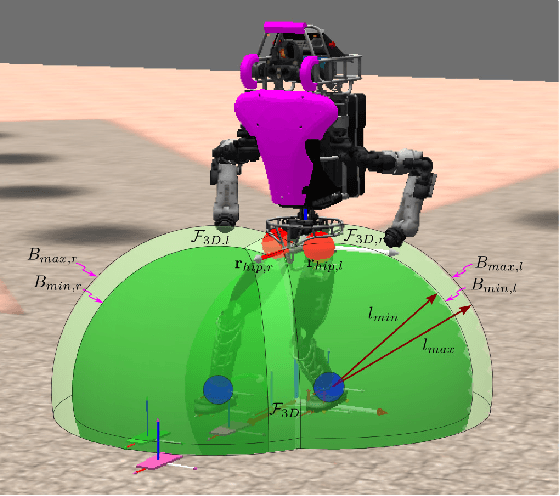
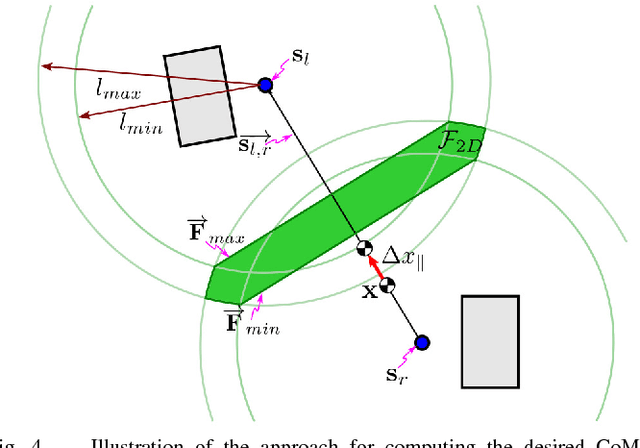
Traditional force-controlled bipedal walking utilizes highly bent knees, resulting in high torques as well as inefficient, and unnatural motions. Even with advanced planning of center of mass height trajectories, significant amounts of knee-bend can be required due to arbitrarily chosen step timing. In this work, we present a method that examines the effects of adjusting the step timing to produce plans that only require a specified amount of knee bend to execute. We define a quadratic program that optimizes the step timings and is executed using a simple iterative feedback approach to account for higher order terms. We then illustrate the effectiveness of this algorithm by comparing the walking gait of the simulated Atlas humanoid with and without the algorithm, showing that the algorithm significantly reduces the required knee bend for execution. We aim to later use this approach to achieve natural, efficient walking motions on humanoid robot platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge