Can We Automate the Analysis of Online Child Sexual Exploitation Discourse?
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2022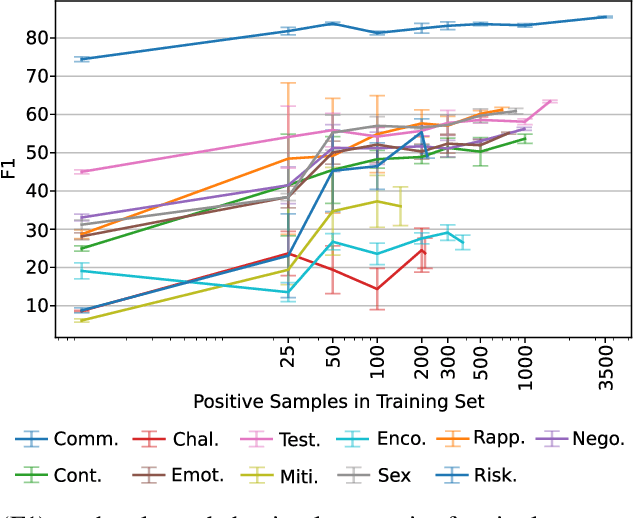

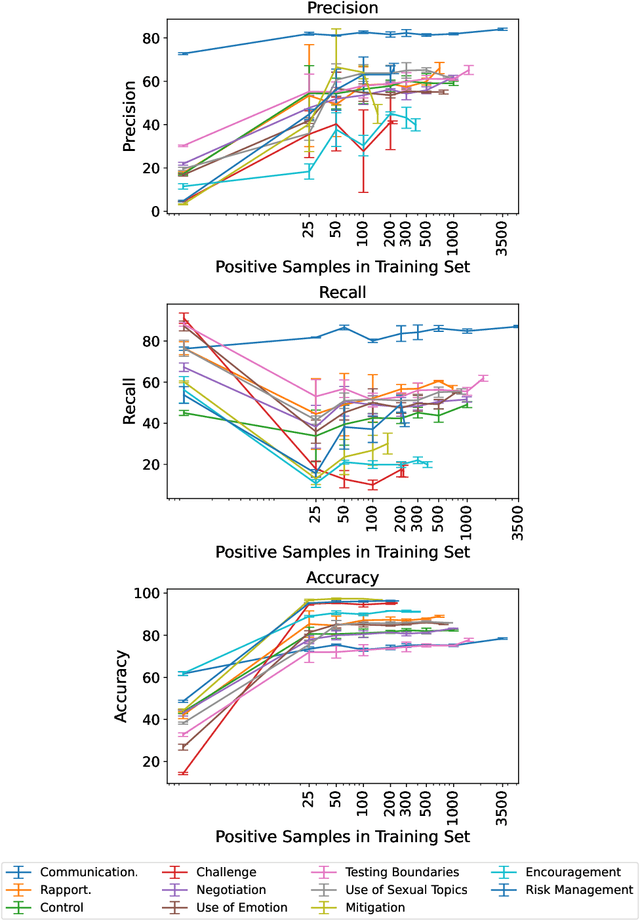

Social media's growing popularity raises concerns around children's online safety. Interactions between minors and adults with predatory intentions is a particularly grave concern. Research into online sexual grooming has often relied on domain experts to manually annotate conversations, limiting both scale and scope. In this work, we test how well-automated methods can detect conversational behaviors and replace an expert human annotator. Informed by psychological theories of online grooming, we label $6772$ chat messages sent by child-sex offenders with one of eleven predatory behaviors. We train bag-of-words and natural language inference models to classify each behavior, and show that the best performing models classify behaviors in a manner that is consistent, but not on-par, with human annotation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge