Can LLMs Converse Formally? Automatically Assessing LLMs in Translating and Interpreting Formal Specifications
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2024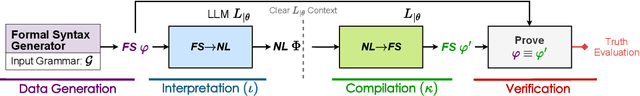
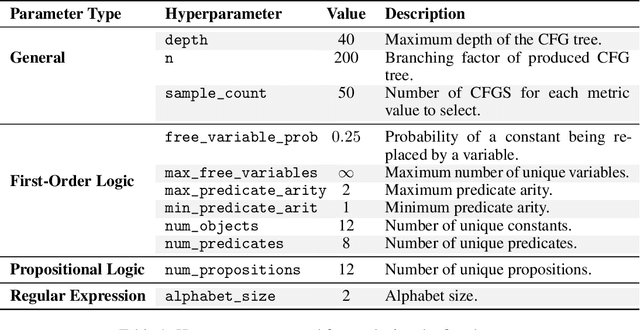
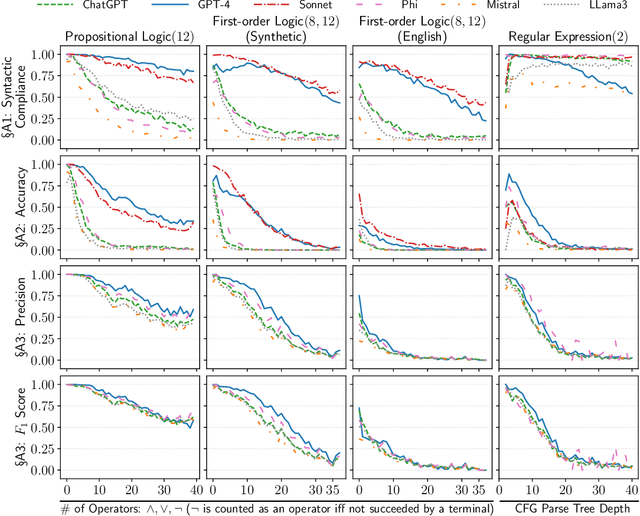
Stakeholders often describe system requirements using natural language which are then converted to formal syntax by a domain-expert leading to increased design costs. This paper assesses the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in converting between natural language descriptions and formal specifications. Existing work has evaluated the capabilities of LLMs in generating formal syntax such as source code but such experiments are typically hand-crafted and use problems that are likely to be in the training set of LLMs, and often require human-annotated datasets. We propose an approach that can use two copies of an LLM in conjunction with an off-the-shelf verifier to automatically evaluate its translation abilities without any additional human input. Our approach generates formal syntax using language grammars to automatically generate a dataset. We conduct an empirical evaluation to measure the accuracy of this translation task and show that SOTA LLMs cannot adequately solve this task, limiting their current utility in the design of complex systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge