Can domain adaptation make object recognition work for everyone?
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2022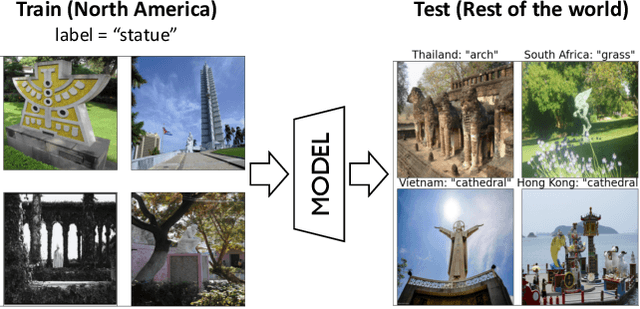



Despite the rapid progress in deep visual recognition, modern computer vision datasets significantly overrepresent the developed world and models trained on such datasets underperform on images from unseen geographies. We investigate the effectiveness of unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) of such models across geographies at closing this performance gap. To do so, we first curate two shifts from existing datasets to study the Geographical DA problem, and discover new challenges beyond data distribution shift: context shift, wherein object surroundings may change significantly across geographies, and subpopulation shift, wherein the intra-category distributions may shift. We demonstrate the inefficacy of standard DA methods at Geographical DA, highlighting the need for specialized geographical adaptation solutions to address the challenge of making object recognition work for everyone.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge