Bridging the Gap for Test-Time Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
Paper and Code
Dec 10, 2024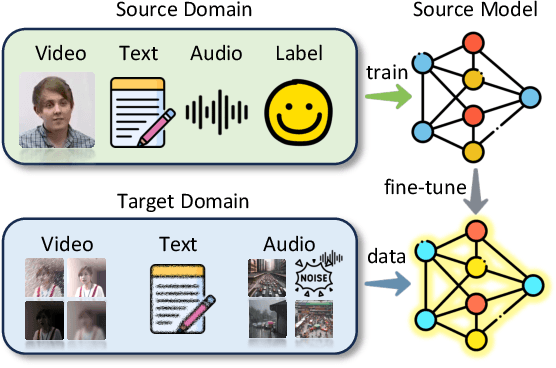
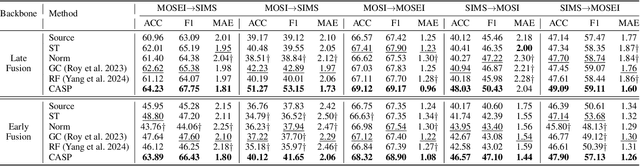

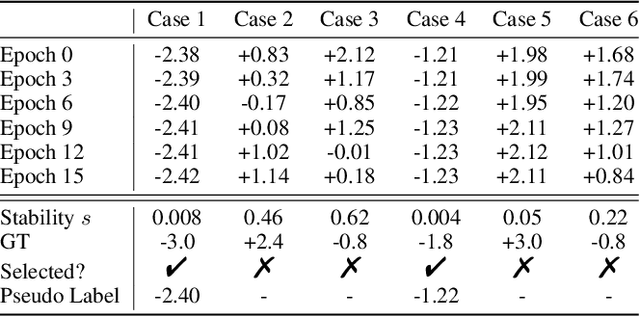
Multimodal sentiment analysis (MSA) is an emerging research topic that aims to understand and recognize human sentiment or emotions through multiple modalities. However, in real-world dynamic scenarios, the distribution of target data is always changing and different from the source data used to train the model, which leads to performance degradation. Common adaptation methods usually need source data, which could pose privacy issues or storage overheads. Therefore, test-time adaptation (TTA) methods are introduced to improve the performance of the model at inference time. Existing TTA methods are always based on probabilistic models and unimodal learning, and thus can not be applied to MSA which is often considered as a multimodal regression task. In this paper, we propose two strategies: Contrastive Adaptation and Stable Pseudo-label generation (CASP) for test-time adaptation for multimodal sentiment analysis. The two strategies deal with the distribution shifts for MSA by enforcing consistency and minimizing empirical risk, respectively. Extensive experiments show that CASP brings significant and consistent improvements to the performance of the model across various distribution shift settings and with different backbones, demonstrating its effectiveness and versatility. Our codes are available at https://github.com/zrguo/CASP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge