Bridging Graph Neural Networks and Statistical Relational Learning: Relational One-Class GCN
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2021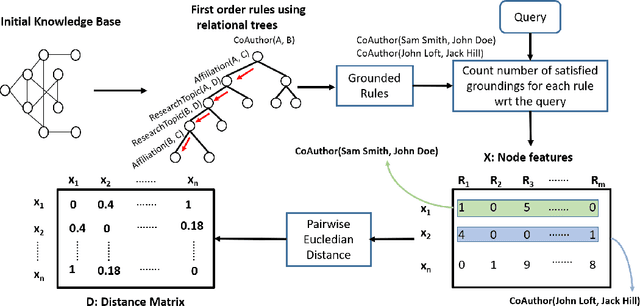

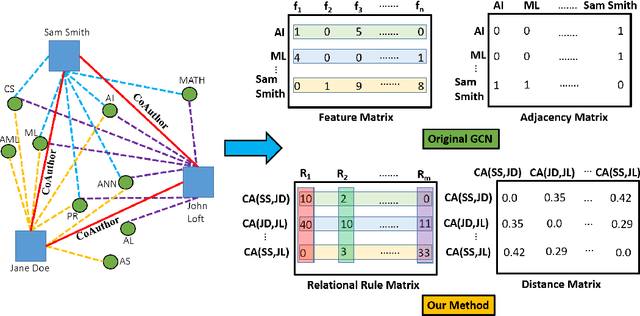
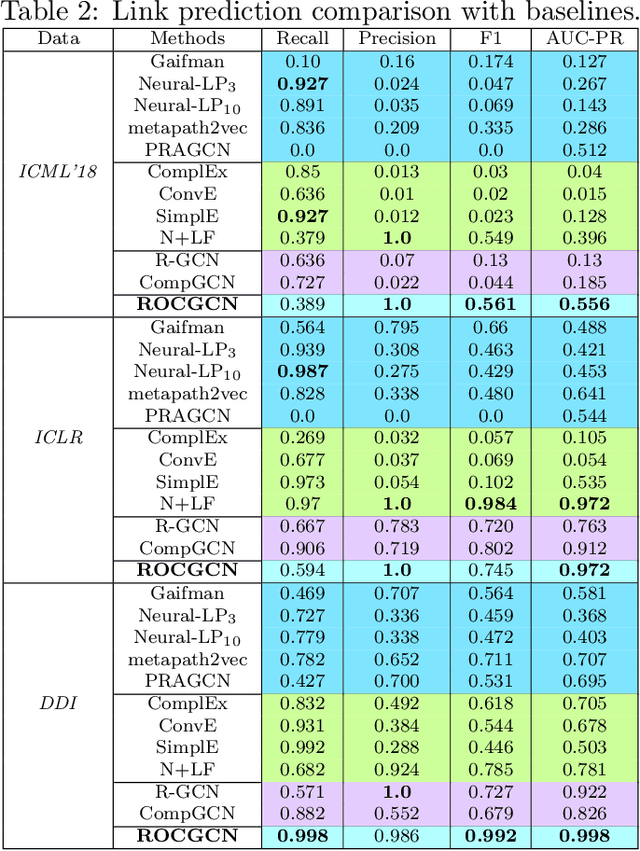
We consider the problem of learning Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) for relational data. Specifically, we consider the classic link prediction and node classification problems as relational modeling tasks and develop a relational extension to GCNs. Our method constructs a secondary graph using relational density estimation techniques where vertices correspond to the target triples. We emphasize the importance of learning features using the secondary graph and the advantages of employing a distance matrix over the typically used adjacency matrix. Our comprehensive empirical evaluation demonstrates the superiority of our approach over $\mathbf{12}$ different GCN models, relational embedding techniques, rule learning techniques and relational models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge