Brain-inspired probabilistic generative model for double articulation analysis of spoken language
Paper and Code
Jul 06, 2022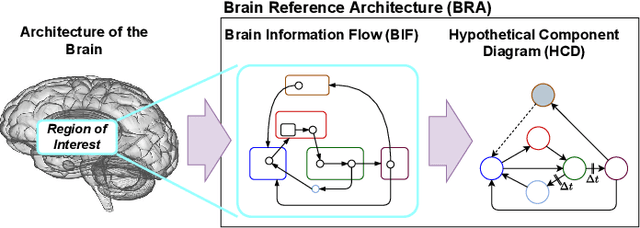
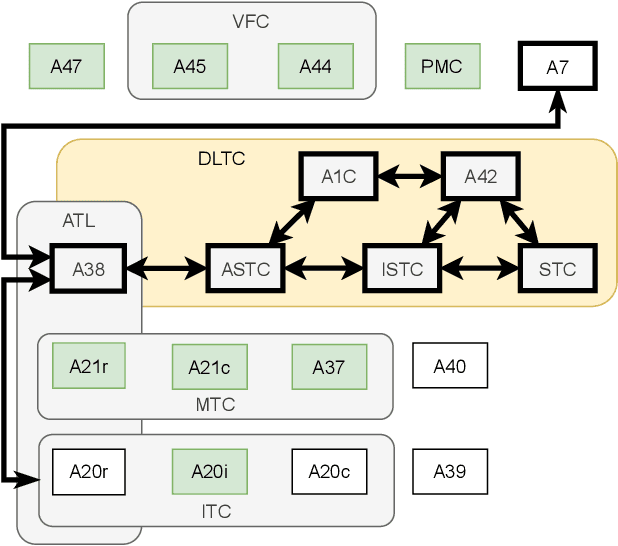
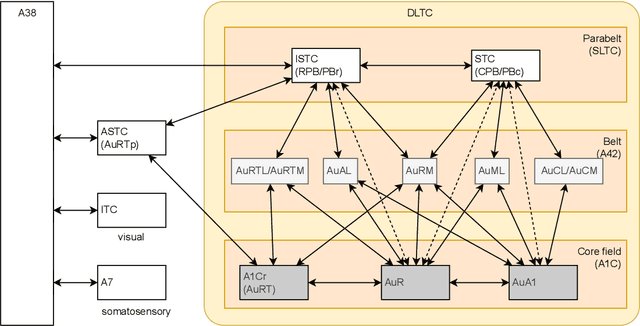
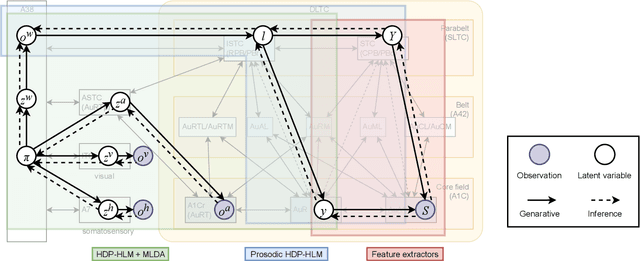
The human brain, among its several functions, analyzes the double articulation structure in spoken language, i.e., double articulation analysis (DAA). A hierarchical structure in which words are connected to form a sentence and words are composed of phonemes or syllables is called a double articulation structure. Where and how DAA is performed in the human brain has not been established, although some insights have been obtained. In addition, existing computational models based on a probabilistic generative model (PGM) do not incorporate neuroscientific findings, and their consistency with the brain has not been previously discussed. This study compared, mapped, and integrated these existing computational models with neuroscientific findings to bridge this gap, and the findings are relevant for future applications and further research. This study proposes a PGM for a DAA hypothesis that can be realized in the brain based on the outcomes of several neuroscientific surveys. The study involved (i) investigation and organization of anatomical structures related to spoken language processing, and (ii) design of a PGM that matches the anatomy and functions of the region of interest. Therefore, this study provides novel insights that will be foundational to further exploring DAA in the brain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge