Boosting Liver and Lesion Segmentation from CT Scans By Mask Mining
Paper and Code
Aug 14, 2019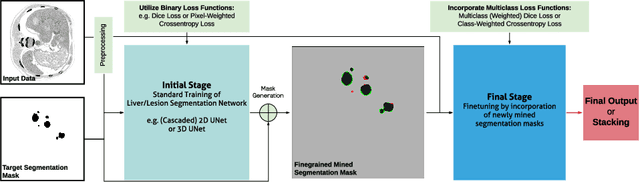


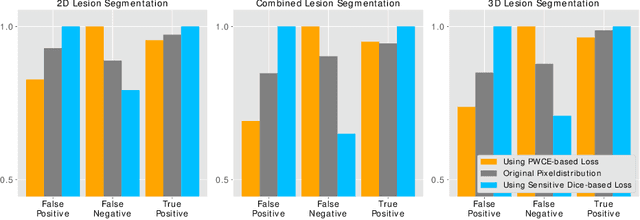
In this paper we propose a novel procedure to improve liver and liver lesion segmentation from CT scans for U-Net based models. Our method is an extension to standard segmentation pipelines allowing for more fine-grained control over the network output by focusing on higher target recall or reduction of noisy false-positive predictions, thereby also boosting overall segmentation performance. To achieve this, we include segmentation errors after a primary learning step into a new learning process appended to the main training setup, allowing the model to find features which explain away previous errors. We evaluate this on distinct architectures including cascaded two- and three-dimensional as well as combined learning setups for multitask segmentation. Liver and lesion segmentation data is provided by the Liver Tumor Segmentationchallenge (LiTS), with an increase in dice score of up to 3 points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge