Bidirectional Semi-supervised Dual-branch CNN for Robust 3D Reconstruction of Stereo Endoscopic Images via Adaptive Cross and Parallel Supervisions
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2022
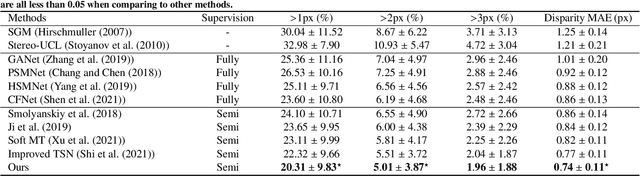

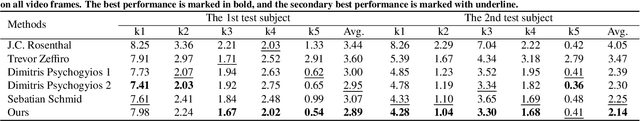
Semi-supervised learning via teacher-student network can train a model effectively on a few labeled samples. It enables a student model to distill knowledge from the teacher's predictions of extra unlabeled data. However, such knowledge flow is typically unidirectional, having the performance vulnerable to the quality of teacher model. In this paper, we seek to robust 3D reconstruction of stereo endoscopic images by proposing a novel fashion of bidirectional learning between two learners, each of which can play both roles of teacher and student concurrently. Specifically, we introduce two self-supervisions, i.e., Adaptive Cross Supervision (ACS) and Adaptive Parallel Supervision (APS), to learn a dual-branch convolutional neural network. The two branches predict two different disparity probability distributions for the same position, and output their expectations as disparity values. The learned knowledge flows across branches along two directions: a cross direction (disparity guides distribution in ACS) and a parallel direction (disparity guides disparity in APS). Moreover, each branch also learns confidences to dynamically refine its provided supervisions. In ACS, the predicted disparity is softened into a unimodal distribution, and the lower the confidence, the smoother the distribution. In APS, the incorrect predictions are suppressed by lowering the weights of those with low confidence. With the adaptive bidirectional learning, the two branches enjoy well-tuned supervisions from each other, and eventually converge on a consistent and more accurate disparity estimation. The extensive and comprehensive experimental results on three public datasets demonstrate our superior performance over the fully-supervised and semi-supervised state-of-the-arts with a decrease of averaged disparity error by 13.95% and 3.90% at least, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge