Bidirectional Quaternion Long-Short Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks for Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2018
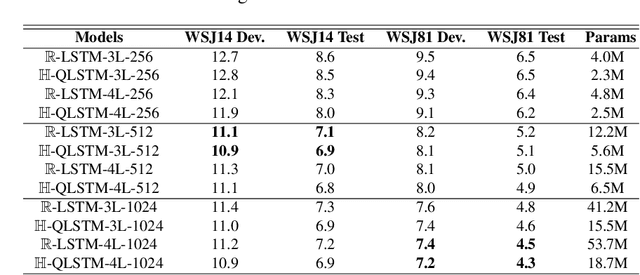
Recurrent neural networks (RNN) are at the core of modern automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. In particular, long-short term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural networks have achieved state-of-the-art results in many speech recognition tasks, due to their efficient representation of long and short term dependencies in sequences of inter-dependent features. Nonetheless, internal dependencies within the element composing multidimensional features are weakly considered by traditional real-valued representations. We propose a novel quaternion long-short term memory (QLSTM) recurrent neural network that takes into account both the external relations between the features composing a sequence, and these internal latent structural dependencies with the quaternion algebra. QLSTMs are compared to LSTMs during a memory copy-task and a realistic application of speech recognition on the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) dataset. QLSTM reaches better performances during the two experiments with up to $2.8$ times less learning parameters, leading to a more expressive representation of the information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge