Biases in In Silico Evaluation of Molecular Optimization Methods and Bias-Reduced Evaluation Methodology
Paper and Code
Jan 28, 2022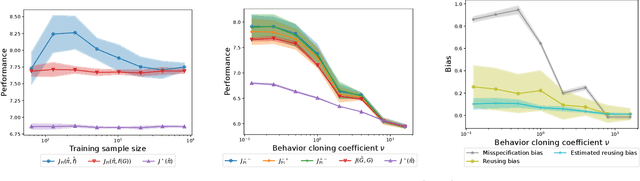
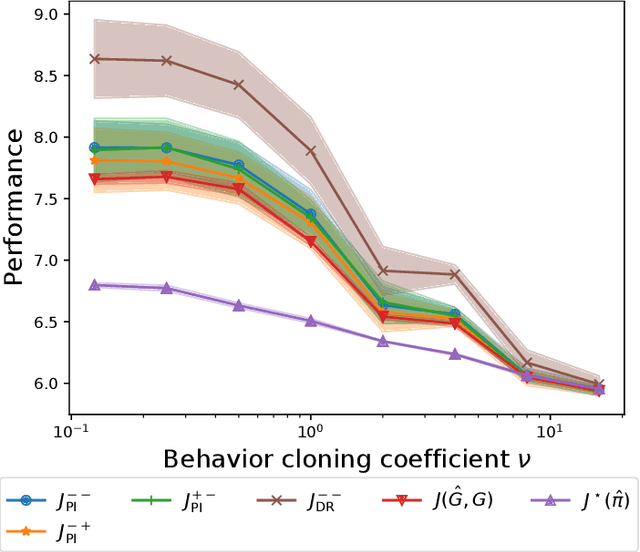
We are interested in in silico evaluation methodology for molecular optimization methods. Given a sample of molecules and their properties of our interest, we wish not only to train an agent that can find molecules optimized with respect to the target property but also to evaluate its performance. A common practice is to train a predictor of the target property on the sample and use it for both training and evaluating the agent. We show that this evaluator potentially suffers from two biases; one is due to misspecification of the predictor and the other to reusing the same sample for training and evaluation. We discuss bias reduction methods for each of the biases comprehensively, and empirically investigate their effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge