Beyond Point Estimate: Inferring Ensemble Prediction Variation from Neuron Activation Strength in Recommender Systems
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2020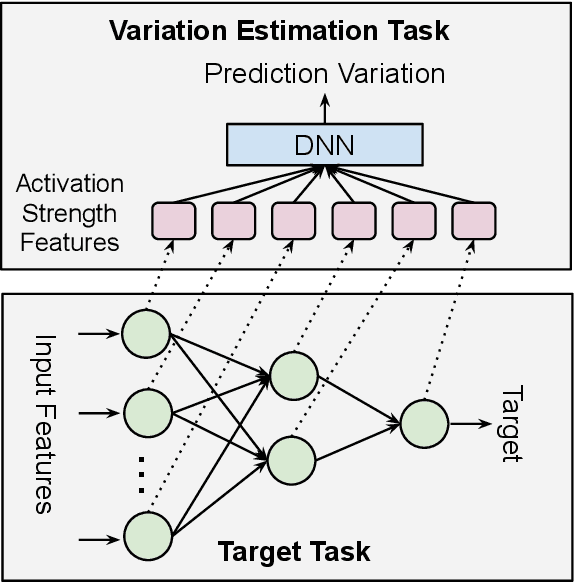
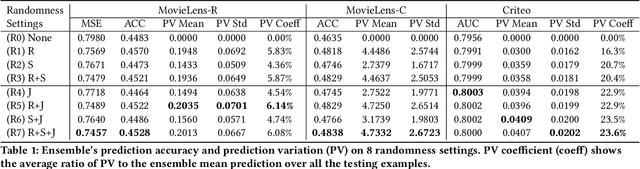
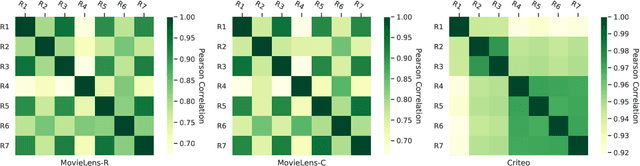
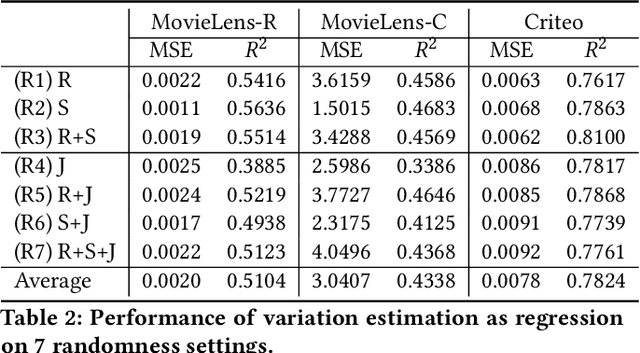
Despite deep neural network (DNN)'s impressive prediction performance in various domains, it is well known now that a set of DNN models trained with the same model specification and the same data can produce very different prediction results. Ensemble method is one state-of-the-art benchmark for prediction uncertainty estimation. However, ensembles are expensive to train and serve for web-scale traffic. In this paper, we seek to advance the understanding of prediction variation estimated by the ensemble method. Through empirical experiments on two widely used benchmark datasets MovieLens and Criteo in recommender systems, we observe that prediction variations come from various randomness sources, including training data shuffling, and parameter random initialization. By introducing more randomness into model training, we notice that ensemble's mean predictions tend to be more accurate while the prediction variations tend to be higher. Moreover, we propose to infer prediction variation from neuron activation strength and demonstrate the strong prediction power from activation strength features. Our experiment results show that the average R squared on MovieLens is as high as 0.56 and on Criteo is 0.81. Our method performs especially well when detecting the lowest and highest variation buckets, with 0.92 AUC and 0.89 AUC respectively. Our approach provides a simple way for prediction variation estimation, which opens up new opportunities for future work in many interesting areas (e.g.,model-based reinforcement learning) without relying on serving expensive ensemble models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge