Beware the Black-Box: on the Robustness of Recent Defenses to Adversarial Examples
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2020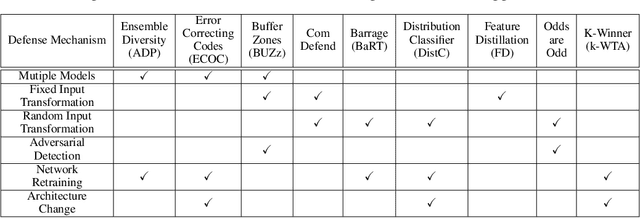
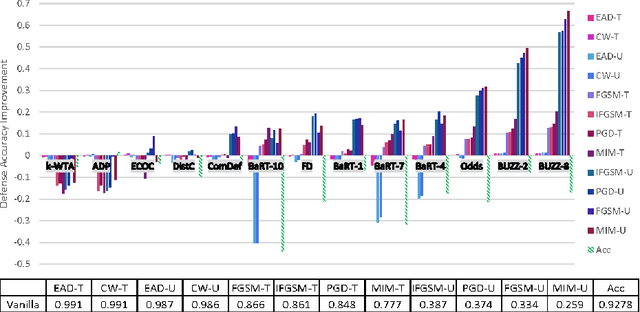
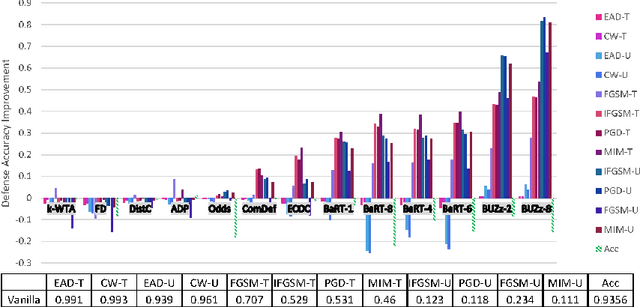
Recent defenses published at venues like NIPS, ICML, ICLR and CVPR are mainly focused on mitigating white-box attacks. These defenses do not properly consider adaptive adversaries. In this paper, we expand the scope of these defenses to include adaptive black-box adversaries. Our evaluation is done on nine defenses including Barrage of Random Transforms, ComDefend, Ensemble Diversity, Feature Distillation, The Odds are Odd, Error Correcting Codes, Distribution Classifier Defense, K-Winner Take All and Buffer Zones. Our investigation is done using two black-box adversarial models and six widely studied adversarial attacks for CIFAR-10 and Fashion-MNIST datasets. Our analyses show most recent defenses provide only marginal improvements in security, as compared to undefended networks. Based on these results, we propose new standards for properly evaluating defenses to black-box adversaries. We provide this security framework to assist researchers in developing future black-box resistant models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge