Benchmarking projective simulation in navigation problems
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2018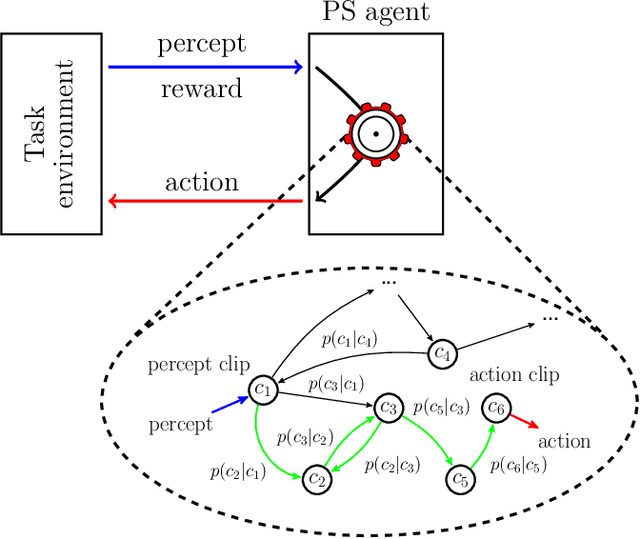
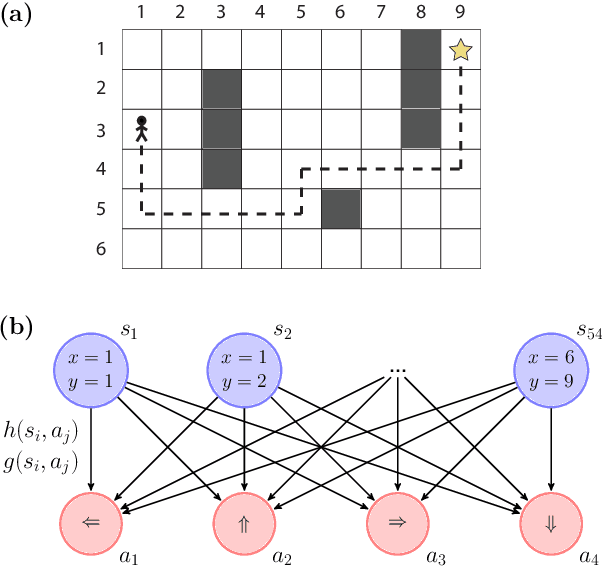
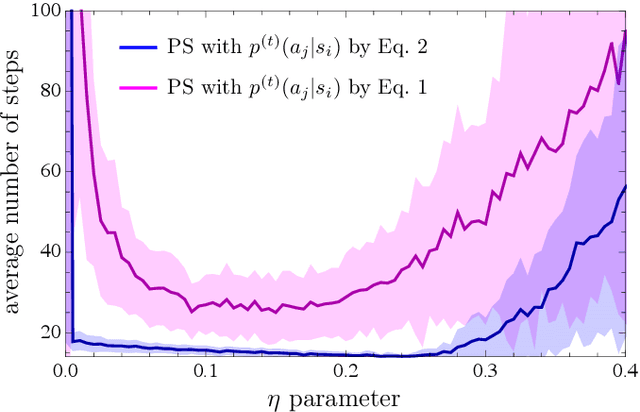
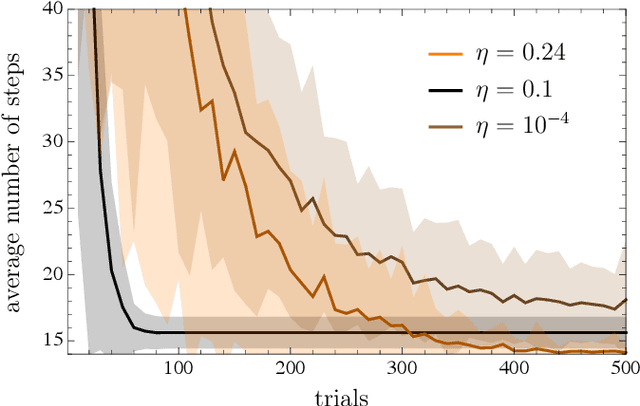
Projective simulation (PS) is a model for intelligent agents with a deliberation capacity that is based on episodic memory. The model has been shown to provide a flexible framework for constructing reinforcement-learning agents, and it allows for quantum mechanical generalization, which leads to a speed-up in deliberation time. PS agents have been applied successfully in the context of complex skill learning in robotics, and in the design of state-of-the-art quantum experiments. In this paper, we study the performance of projective simulation in two benchmarking problems in navigation, namely the grid world and the mountain car problem. The performance of PS is compared to standard tabular reinforcement learning approaches, Q-learning and SARSA. Our comparison demonstrates that the performance of PS and standard learning approaches are qualitatively and quantitatively similar, while it is much easier to choose optimal model parameters in case of projective simulation, with a reduced computational effort of one to two orders of magnitude. Our results show that the projective simulation model stands out for its simplicity in terms of the number of model parameters, which makes it simple to set up the learning agent in unknown task environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge