Beamspace Multidimensional ESPRIT Approaches for Simultaneous Localization and Communications
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2021
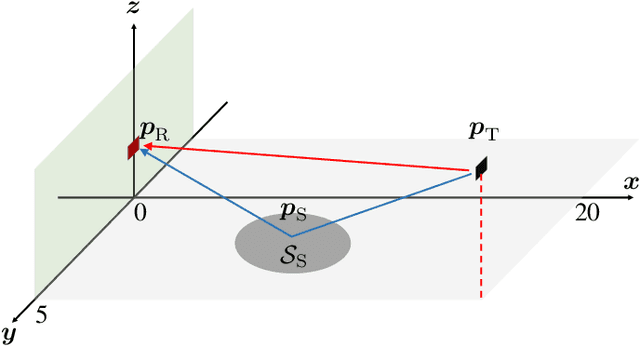

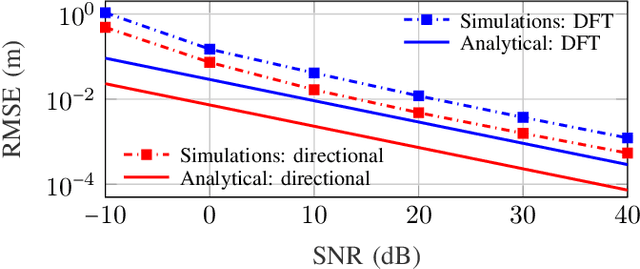
Modern wireless communication systems operating at high carrier frequencies are characterized by a high dimensionality of the underlying parameter space (including channel gains, angles, delays, and possibly Doppler shifts). Estimating these parameters is valuable for communication purposes, but also for localization and sensing, making channel estimation a critical component in any joint communication and localization or sensing application. The high dimensionality make it difficult to use search-based methods such as maximum likelihood. Search-free methods such as ESPRIT provide an attractive alternative, but require a complex decomposition step in both the tensor and matrix version of ESPRIT. To mitigate this, we propose, develop, and analyze a reduced complexity beamspace ESPRIT method. Complexity is reduced both by beampace processing as well as low-complex implementation of the singular value decomposition. A novel perturbation analysis provides important insights for both channel estimation and localization performance. The proposed method is compared to the tensor ESPRIT method, in terms of channel estimation, communication, localization, and sensing performance, further validating the perturbation analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge