Bayesian Differential Privacy through Posterior Sampling
Paper and Code
Dec 23, 2016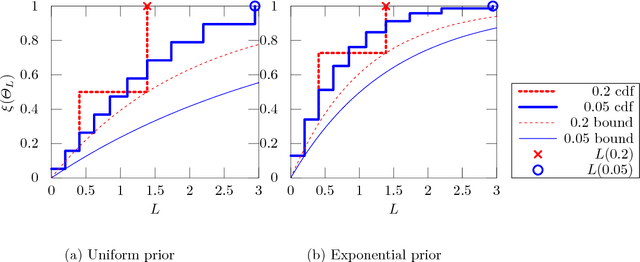
Differential privacy formalises privacy-preserving mechanisms that provide access to a database. We pose the question of whether Bayesian inference itself can be used directly to provide private access to data, with no modification. The answer is affirmative: under certain conditions on the prior, sampling from the posterior distribution can be used to achieve a desired level of privacy and utility. To do so, we generalise differential privacy to arbitrary dataset metrics, outcome spaces and distribution families. This allows us to also deal with non-i.i.d or non-tabular datasets. We prove bounds on the sensitivity of the posterior to the data, which gives a measure of robustness. We also show how to use posterior sampling to provide differentially private responses to queries, within a decision-theoretic framework. Finally, we provide bounds on the utility and on the distinguishability of datasets. The latter are complemented by a novel use of Le Cam's method to obtain lower bounds. All our general results hold for arbitrary database metrics, including those for the common definition of differential privacy. For specific choices of the metric, we give a number of examples satisfying our assumptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge