Bayesian Deep Learning for Remaining Useful Life Estimation via Stein Variational Gradient Descent
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2024
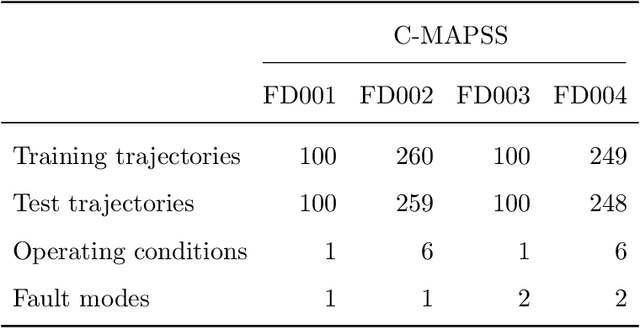
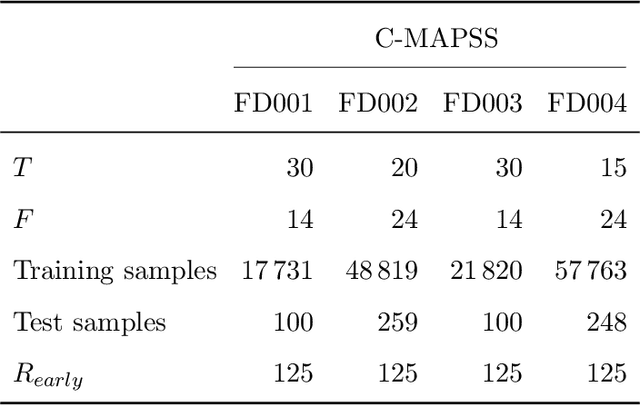
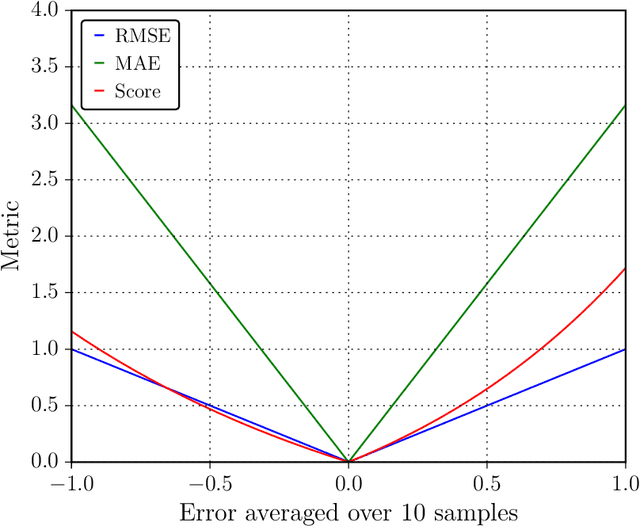
A crucial task in predictive maintenance is estimating the remaining useful life of physical systems. In the last decade, deep learning has improved considerably upon traditional model-based and statistical approaches in terms of predictive performance. However, in order to optimally plan maintenance operations, it is also important to quantify the uncertainty inherent to the predictions. This issue can be addressed by turning standard frequentist neural networks into Bayesian neural networks, which are naturally capable of providing confidence intervals around the estimates. Several methods exist for training those models. Researchers have focused mostly on parametric variational inference and sampling-based techniques, which notoriously suffer from limited approximation power and large computational burden, respectively. In this work, we use Stein variational gradient descent, a recently proposed algorithm for approximating intractable distributions that overcomes the drawbacks of the aforementioned techniques. In particular, we show through experimental studies on simulated run-to-failure turbofan engine degradation data that Bayesian deep learning models trained via Stein variational gradient descent consistently outperform with respect to convergence speed and predictive performance both the same models trained via parametric variational inference and their frequentist counterparts trained via backpropagation. Furthermore, we propose a method to enhance performance based on the uncertainty information provided by the Bayesian models. We release the source code at https://github.com/lucadellalib/bdl-rul-svgd.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge