Basic syntax from speech: Spontaneous concatenation in unsupervised deep neural networks
Paper and Code
May 02, 2023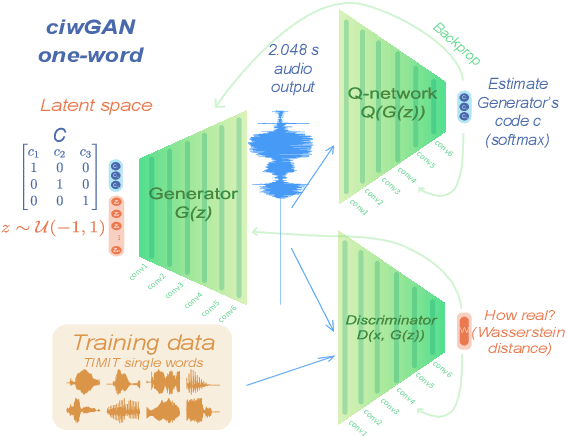
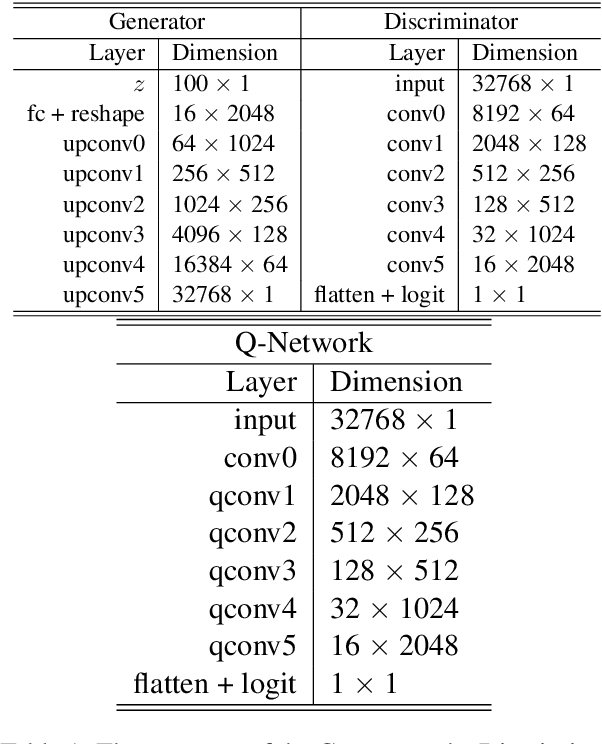
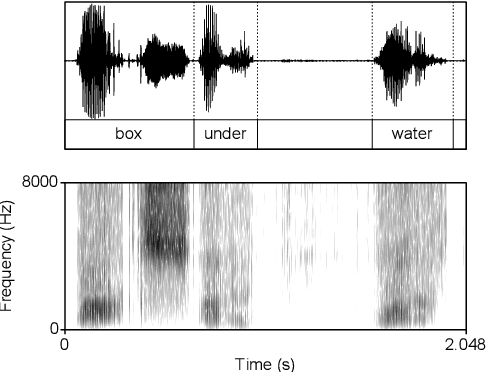
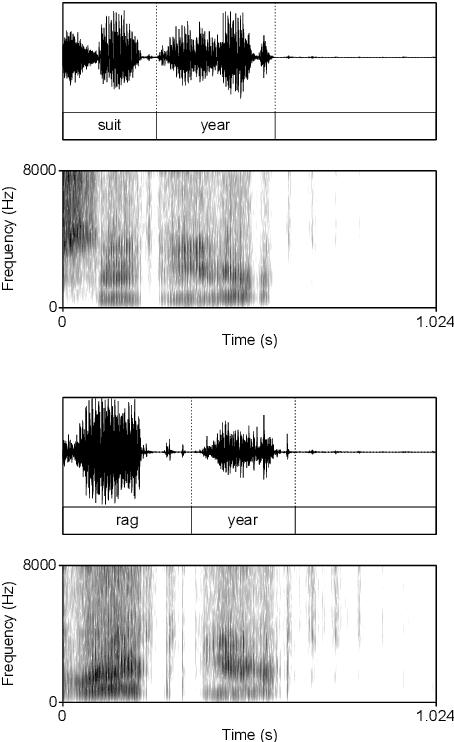
Computational models of syntax are predominantly text-based. Here we propose that basic syntax can be modeled directly from raw speech in a fully unsupervised way. We focus on one of the most ubiquitous and basic properties of syntax -- concatenation. We introduce spontaneous concatenation: a phenomenon where convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on acoustic recordings of individual words start generating outputs with two or even three words concatenated without ever accessing data with multiple words in the input. Additionally, networks trained on two words learn to embed words into novel unobserved word combinations. To our knowledge, this is a previously unreported property of CNNs trained on raw speech in the Generative Adversarial Network setting and has implications both for our understanding of how these architectures learn as well as for modeling syntax and its evolution from raw acoustic inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge