Balanced Ranking with Diversity Constraints
Paper and Code
Jun 04, 2019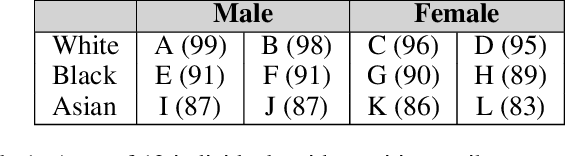
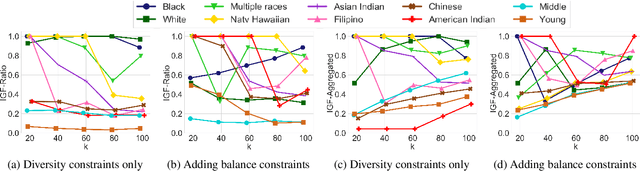
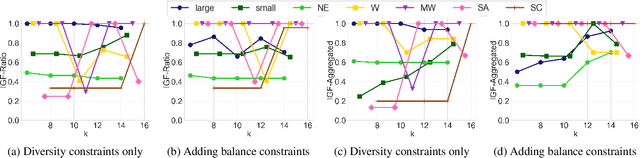
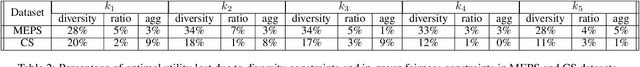
Many set selection and ranking algorithms have recently been enhanced with diversity constraints that aim to explicitly increase representation of historically disadvantaged populations, or to improve the overall representativeness of the selected set. An unintended consequence of these constraints, however, is reduced in-group fairness: the selected candidates from a given group may not be the best ones, and this unfairness may not be well-balanced across groups. In this paper we study this phenomenon using datasets that comprise multiple sensitive attributes. We then introduce additional constraints, aimed at balancing the \in-group fairness across groups, and formalize the induced optimization problems as integer linear programs. Using these programs, we conduct an experimental evaluation with real datasets, and quantify the feasible trade-offs between balance and overall performance in the presence of diversity constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge