B-SCST: Bayesian Self-Critical Sequence Training for Image Captioning
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2020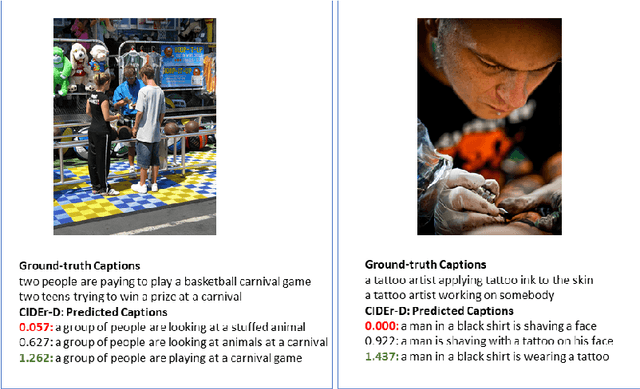
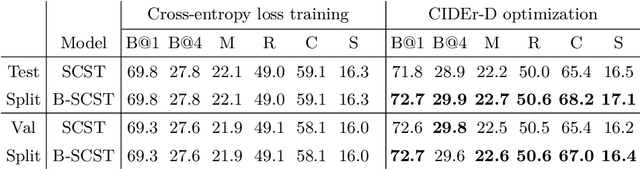
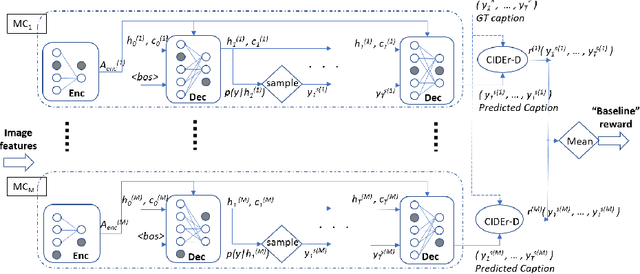
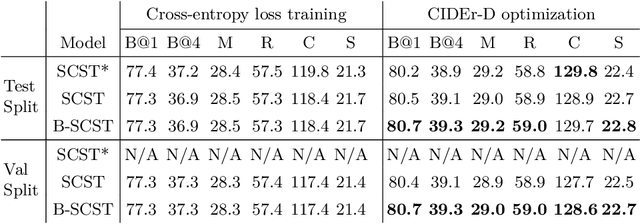
Bayesian deep neural networks (DNN) provide a mathematically grounded framework to quantify uncertainty in their predictions. We propose a Bayesian variant of policy-gradient based reinforcement learning training technique for image captioning models to directly optimize non-differentiable image captioning quality metrics such as CIDEr-D. We extend the well-known Self-Critical Sequence Training (SCST) approach for image captioning models by incorporating Bayesian inference, and refer to it as B-SCST. The "baseline" reward for the policy-gradients in B-SCST is generated by averaging predictive quality metrics (CIDEr-D) of the captions drawn from the distribution obtained using a Bayesian DNN model. This predictive distribution is inferred using Monte Carlo (MC) dropout, which is one of the standard ways to approximate variational inference. We observe that B-SCST improves all the standard captioning quality scores on both Flickr30k and MS COCO datasets, compared to the SCST approach. We also provide a detailed study of uncertainty quantification for the predicted captions, and demonstrate that it correlates well with the CIDEr-D scores. To our knowledge, this is the first such analysis, and it can pave way to more practical image captioning solutions with interpretable models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge